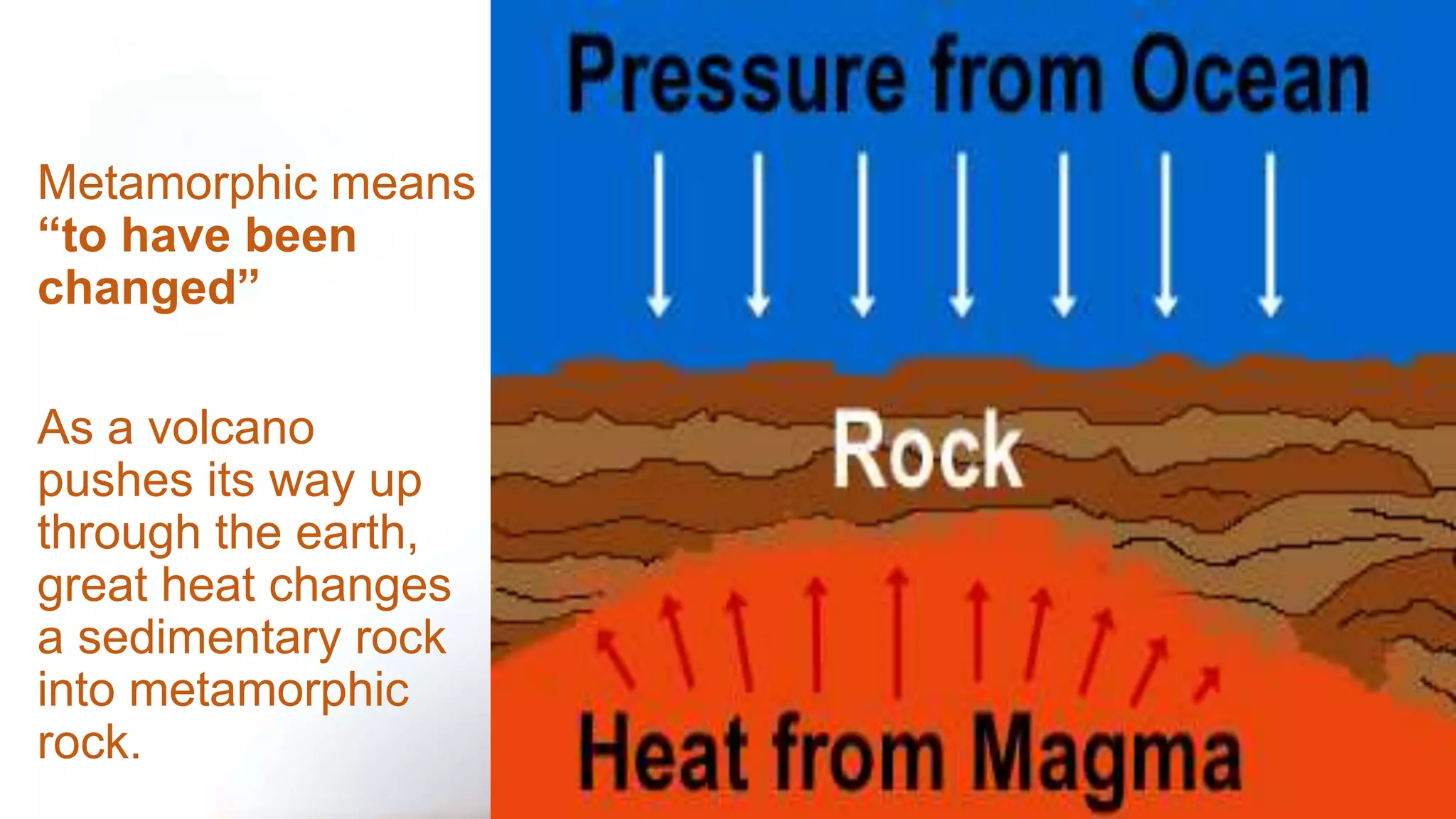
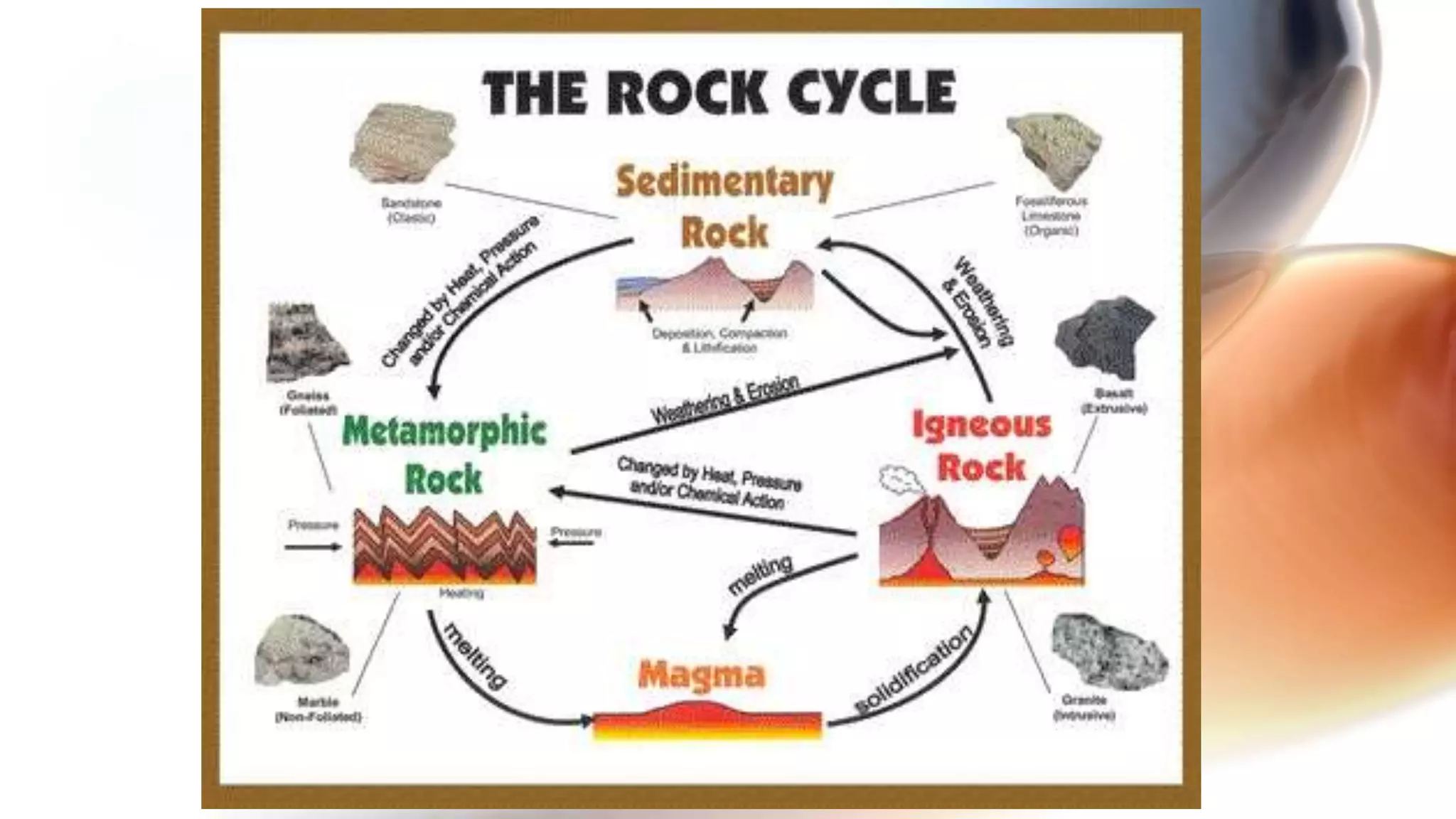
The document discusses the three main types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks form from cooling lava. Sedimentary rocks like limestone and sandstone form from compressed sediments. Metamorphic rocks like marble and slate form from existing rocks that are changed by heat and pressure. Rocks are constantly being recycled through this rock cycle as their components are transformed from one rock type to another through volcanic activity and plate tectonics.