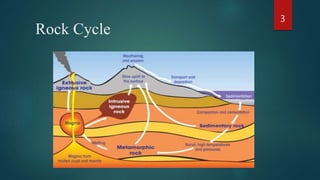
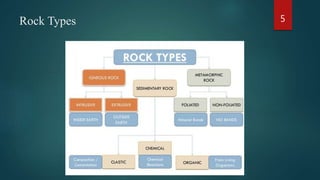
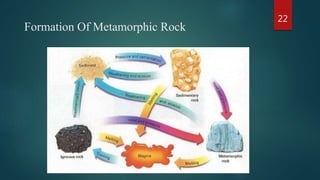
The document discusses the three main types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. It describes the rock cycle whereby rocks constantly change from one type to another through geological forces. Igneous rocks form from molten rock and can be intrusive or extrusive. Sedimentary rocks form through the compaction and cementation of sediments and can be clastic or non-clastic. Metamorphic rocks form from heat and pressure acting on existing rocks, either through contact metamorphism near magma or regional metamorphism during tectonic activity.