This document provides an overview of robotics and automation. It defines a robot and the key elements in a robotics system. Robots are classified based on their physical configuration, including Cartesian, cylindrical, polar and jointed arm configurations. The document discusses the applications of robotics in material handling, processing, assembly and inspection. It also outlines the advantages and disadvantages of robots and automation. Numerical control and computer numerical control machines are described as a form of programmable automation.

![ROBOTICS
“A Robot is a programmable, multi-functional
manipulator designed to move materials, parts, tools
or special devices through variable programmed
motions for performing variety of tasks”
“Robotics is the field of technology that deals with the
conception, design, construction, operation and
application of robots”
Elements of a Robotics system are:
The manipulator, End effectors, Actuators, Transmission
elements
Control system consisting of Controls [Mechanical,
Electrical, Pneumatic, Hydraulic etc.]
Sensors and Equipment interfaces
Computer systems to carry out programming
Power Source [battery/pneumatic/hydraulic etc]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/roboticsautomation-180421032859/85/Robotics-and-Automation-2-320.jpg)
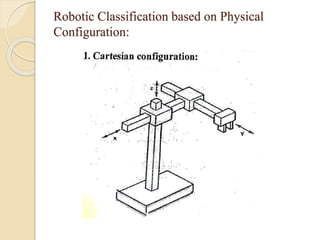
![ Cartesian Configuration [Rectilinear]:
It consists of 3 orthogonal slides namely X, Y & Z axes of the
Cartesian coordinate system
By appropriate movement, the arm of the Robot can move at any
point in the 3-dimensional rectangular spaced work space
Advantages:
o Allows for simpler control
o Possesses high degree of mechanical rigidity
o Can carry heavy loads and the lifting capability does not vary within
the work envelop
Disadvantages:
o Reduced flexibility
o Limitation in the movement of the robotic arm to a small rectangular
work space
Finds application in assembly, machining, inspection, welding etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/roboticsautomation-180421032859/85/Robotics-and-Automation-4-320.jpg)
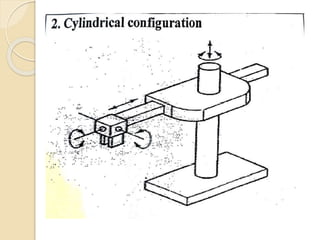
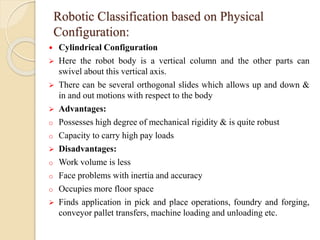
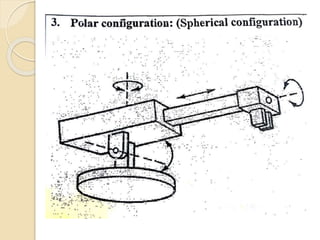
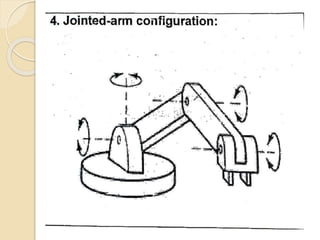
![Robotic Classification based on Physical
Configuration:
Polar Configuration [Spherical]
Here the robot body has a rotary base and a pivot that can be used to
raise and lower a telescopic arm
Within the workspace, it can move its arm in a partial sphere hence
also termed as using spherical coordinates
Advantages:
o Long reach capability in horizontal position
o Increased work envelop with increased work lifting capability
Disadvantages:
o Vertical reach is low
o Lesser rigidity with complex controls
o Problem with inertia and accuracy
Finds application in die casting, forging, injection molding, cleaning
of parts, dip coating etc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/roboticsautomation-180421032859/85/Robotics-and-Automation-8-320.jpg)
![Application of Robotics:
1. Material/Part handling
2. Processing
3. Assembly
4. Inspection
1. Material/Part handling:
Pick and place
Palletizing/de-palletizing[stacking/un-stacking]
Machine loading and/or unloading
Stacking and insertion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/roboticsautomation-180421032859/85/Robotics-and-Automation-11-320.jpg)



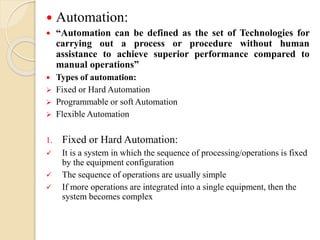
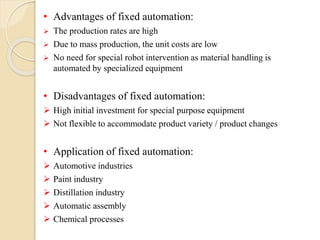
![2. Programmable automation:
Here the production equipment is designed with the capability to
change the sequence of operations to accommodate different product
configurations
The sequence of operations is controlled by a program [set of coded
instructions]
New programs can be prepared and entered into the equipment to
produce new products
• Advantages of Programmable automation:
Most suitable for batch production
Flexibility to deal with changes in the product configuration
• Disadvantages of Programmable automation:
High investment in general-purpose equipment
Low production rates compared to fixed automation
• Applications: In food processing, foundry, textile using NC
machines and PLC’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/roboticsautomation-180421032859/85/Robotics-and-Automation-17-320.jpg)
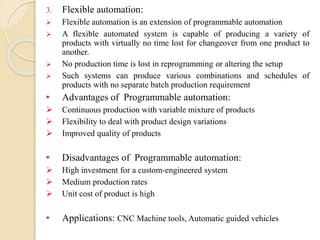
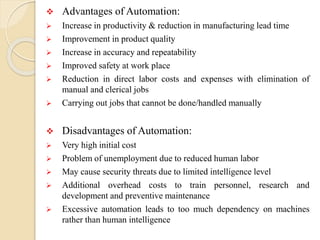


![ Disadvantages of NC machines:
High investment [NC machines costing 5-6 times the conventional
machines]
High spares and maintenance cost
Requirement of special tooling
Need for initial training of operators and up gradation of knowledge
and software
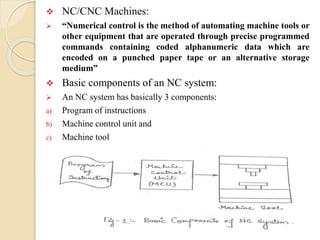
Computer numerical control machine [CNC]:
CNC is an advanced form of NC machine where the machine control
unit is a dedicated microcomputer instead of a hard wired controller
as is in a NC machine. A CNC machine consists of the following:
a) Input device
b) MCU or Machine Control Unit
c) Machine tool
d) Driving system
e) Feedback devices
f) Display unit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/roboticsautomation-180421032859/85/Robotics-and-Automation-23-320.jpg)
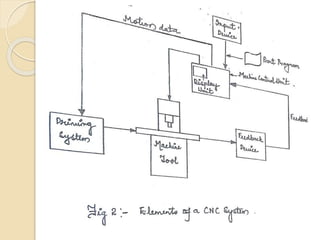
![1. Input Device: The part program is entered into the CNC control
or MCU through the input device. The various input devices are:
i. USB flash drive
ii. Serial communication port that connects with a computer through an
interface
iii. Ethernet communication which is a more reliable and efficient
means of communication
iv. Conversational programming that allows to enter the program
manually
2. Machine control unit [MCU]: The MCU is the heart of a
CNC system which consists of the following:
a) Central processing unit [CPU] which:
i. Has a control section to fetch the data from memory and generates
signals to activate all MCU components
ii. Arithmetic logic unit [ALU] that performs integer and logical
operations
iii. Immediate access memory that holds the data and programs
temporarily as required at the instant by the control section](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/roboticsautomation-180421032859/85/Robotics-and-Automation-25-320.jpg)