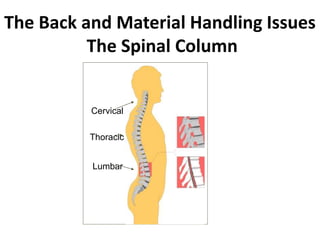
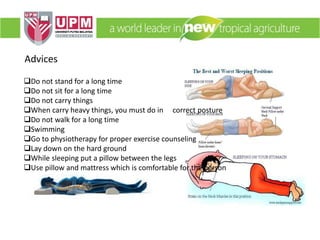
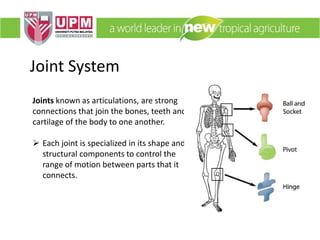
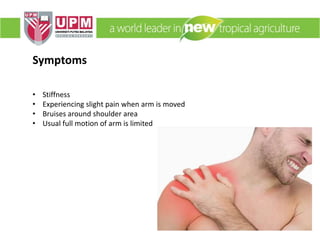
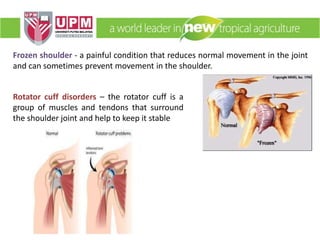
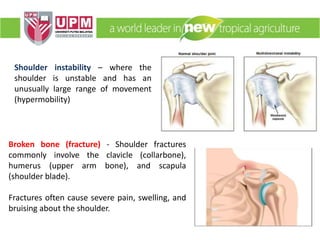
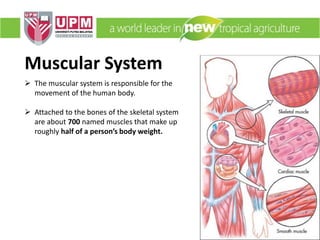
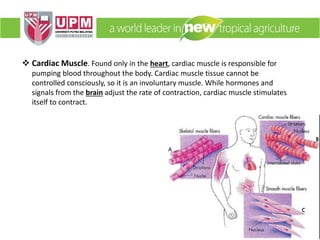
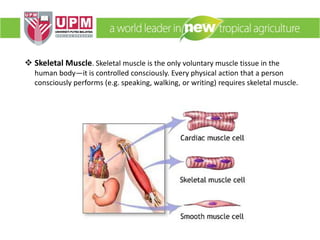
The document discusses industrial ergonomics, focusing on the relationship between biomechanics, work physiology, and musculoskeletal disorders (MSD) caused by repetitive motions and poor posture. It highlights the prevalence of back pain and shoulder issues among workers, outlining causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies such as exercise, proper lifting techniques, and ergonomic adjustments. Additionally, it describes the types of muscle tissue and their roles in human movement, concluding with the importance of understanding biomechanics in preventing MSD.
![Industrial Ergonomics…..[EMM 5710 ]
Lecturer : DR. Eris Elianddy Bin Supeni
Presented by
Group No.5
Name Matric No.
1) Ghassan Maan Salim……………………GS42930
2) Zaid Kh. Saadon………..…………………GS40746
Biomechanics and Work Physiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ergonomicspresentationn-151117205840-lva1-app6891/75/Ergonomics-1-2048.jpg)