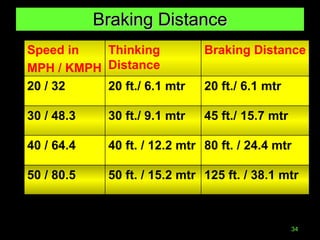
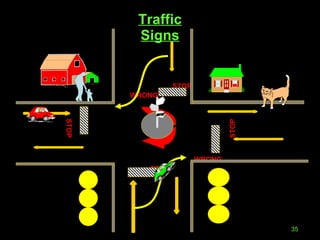
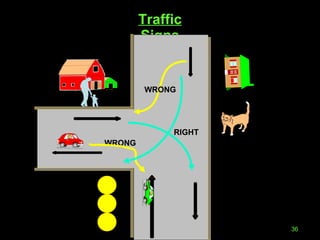
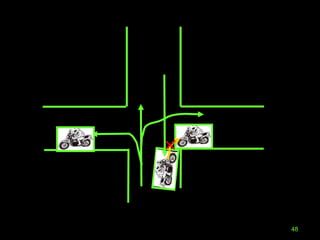
The document outlines essential road safety guidelines and regulations based on the Motor Vehicle Acts in India, emphasizing the importance of wearing helmets, obeying traffic signals, and maintaining safe distances while driving. It highlights the global statistics on road accidents, the significance of defensive driving, and the necessity for awareness of surrounding conditions. It also discusses common unsafe practices and conditions that lead to accidents, promoting better driving habits for the safety of all road users.