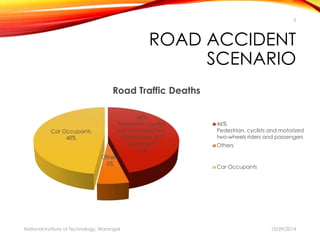
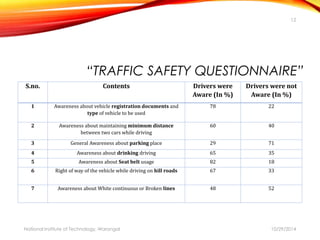
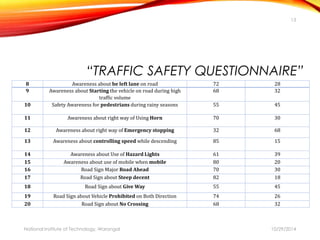
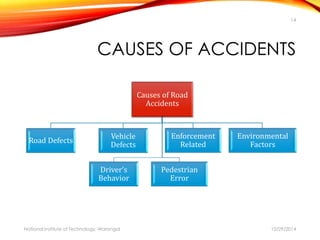
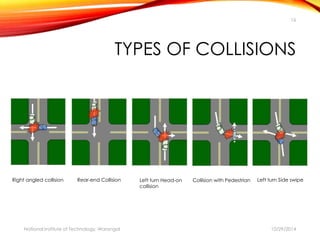
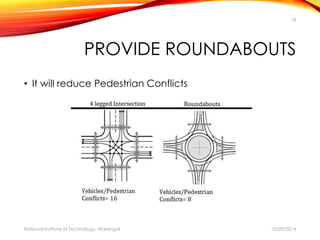
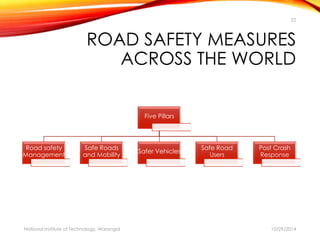
The document discusses a comprehensive approach to road safety, emphasizing the need for improved regulations and public awareness to address the high rate of traffic accidents, particularly in India. It outlines causes of accidents, identifies problems with current systems, and proposes solutions such as state road safety councils and better enforcement of traffic laws. Additionally, it highlights global issues regarding road traffic injuries and the United Nations' efforts to promote road safety measures worldwide.