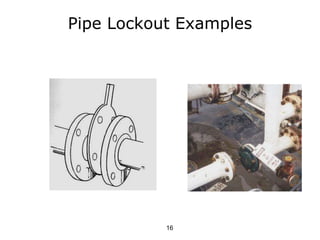
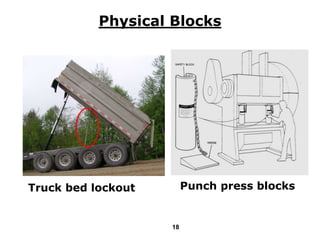
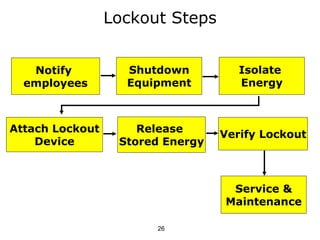
This document discusses lockout/tagout procedures for working on hazardous equipment. It covers who needs training in lockout/tagout, what hazardous energy is, the different types of lockout devices, tag requirements, and required lockout procedures. The procedures involve notifying affected employees, shutting down and isolating equipment, attaching lockout devices, releasing stored energy, and verifying isolation before starting maintenance. Examples of lockout devices include locks for electrical panels and plugs, blanks for pipes, and blocks for presses. Tags are only for information and don't provide the protection of lockout devices.