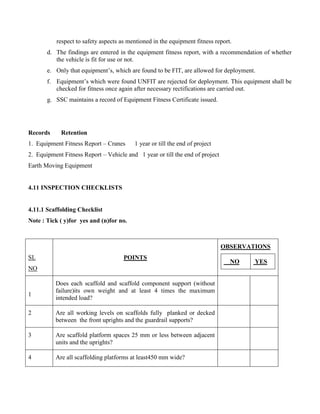
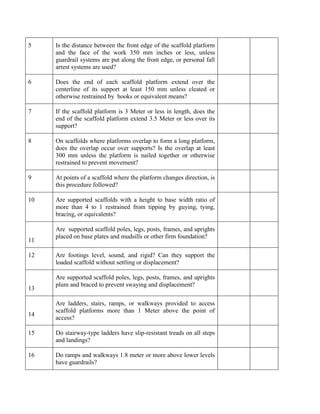
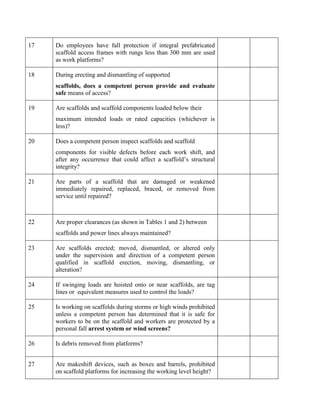
This document provides safety guidelines for working with various types of construction machinery. It outlines requirements for siting machinery safely, fencing dangerous parts, providing safe access, and conducting maintenance and inspections. Specific guidelines are provided for earth moving, lifting, and hoisting machinery. Drivers and signalers must be trained and competent. Machinery must be tested regularly and thoroughly inspected for defects before each shift to ensure safe operation.