This document discusses road safety issues in India. Some key points:
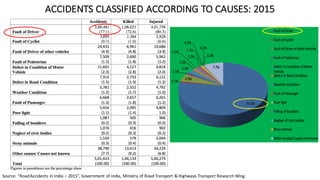
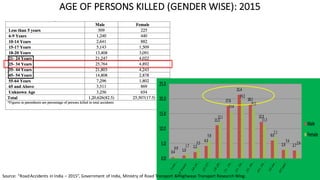
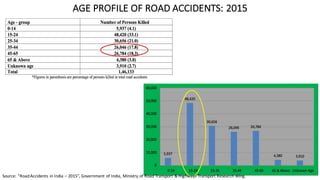
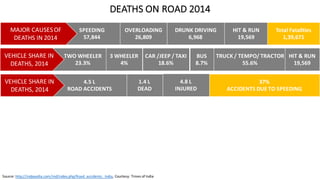
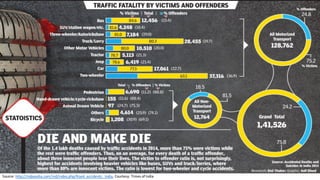
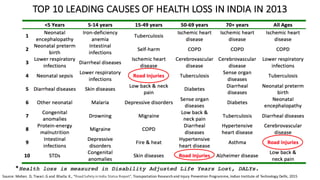
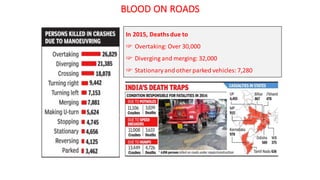
- One death occurs on Indian roads every four minutes, with over 137,000 deaths in 2013. Common causes of accidents include speeding, drunk driving, and overloading of vehicles.
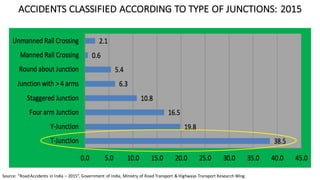
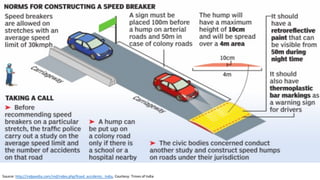
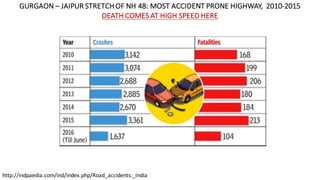
- The top cities for road deaths are Delhi, Chennai, Jaipur, Bengaluru, and Mumbai. Accident rates have been increasing over the past decade. Specific engineering issues like median barriers and road construction also contribute to accidents.