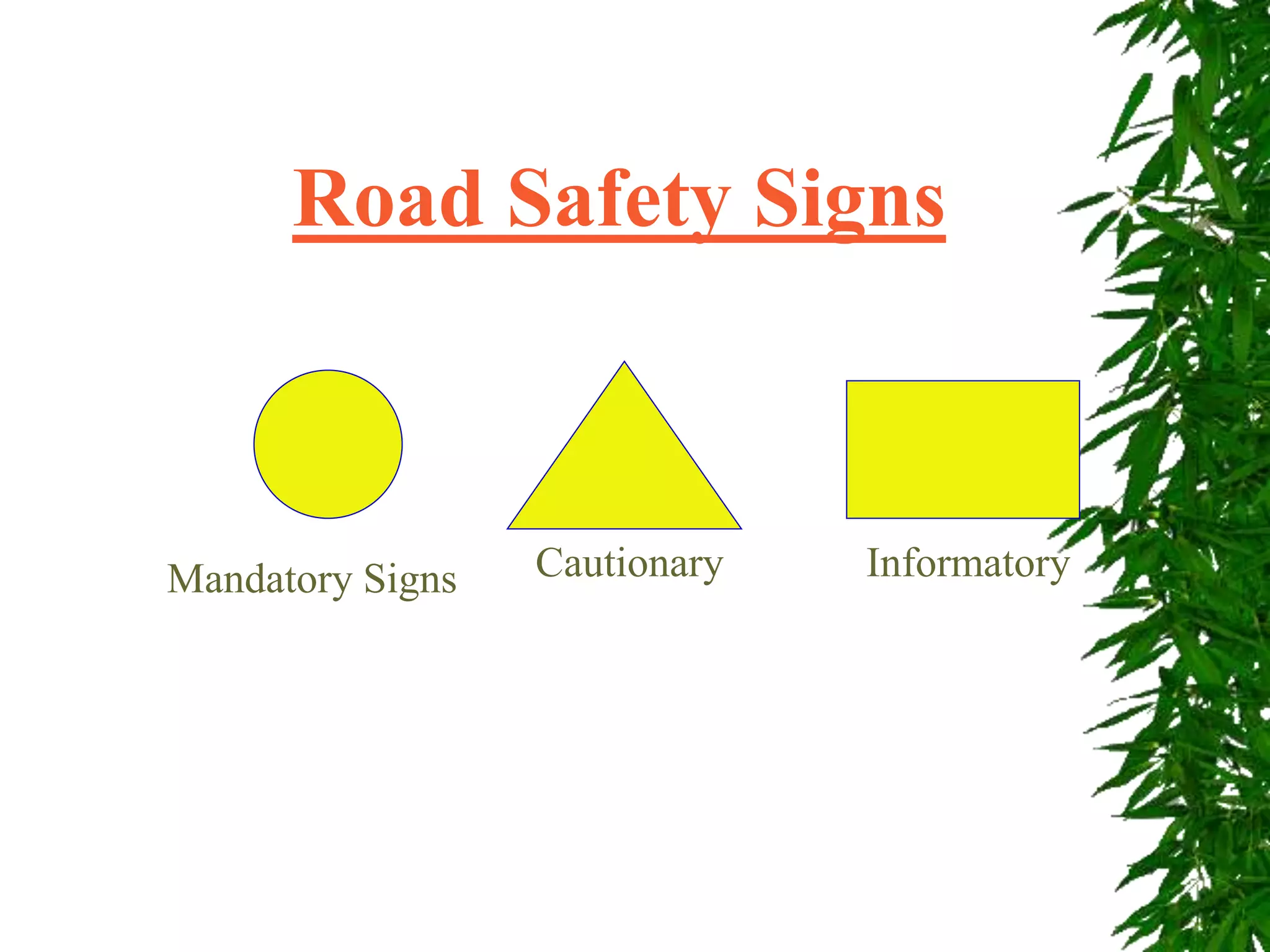
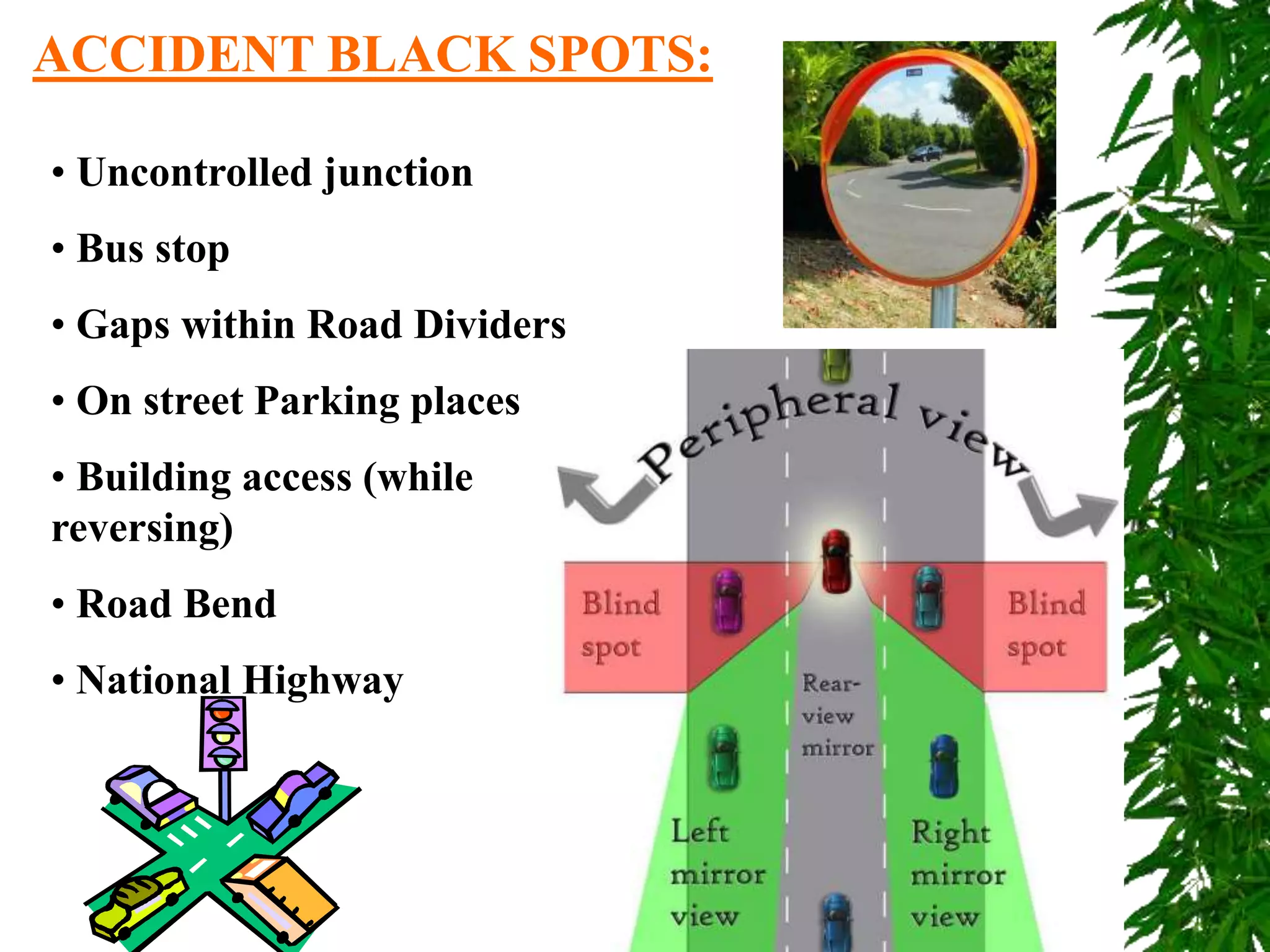
Road safety is important in India because road accidents are one of the leading causes of death. With more vehicles on roads, everyone must follow traffic rules and be aware of safety. Various signs and devices help control traffic and guide drivers, but accidents still occur frequently due to issues with drivers, vehicles, and road conditions. Defensive driving techniques can help save lives by driving carefully despite risks created by others and the environment.