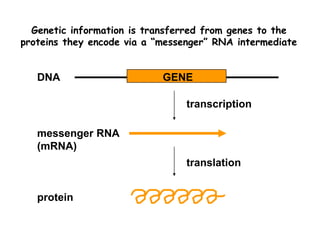
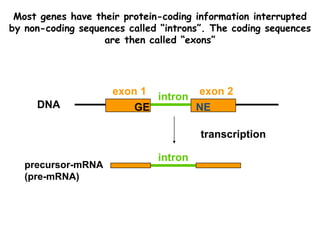
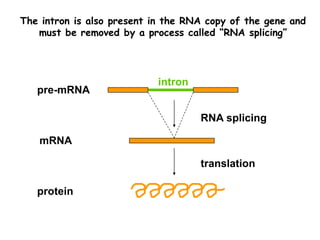
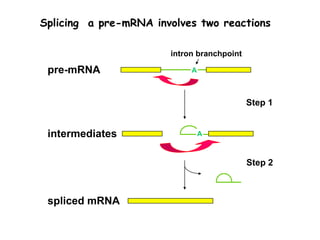
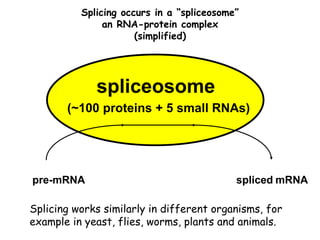
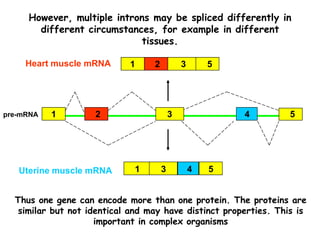
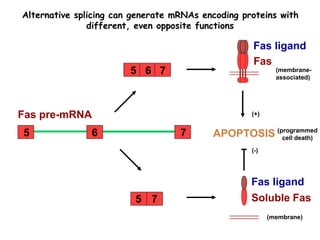
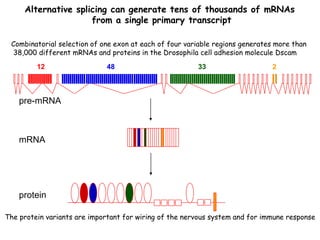
RNA splicing is the process by which introns, or non-coding sequences, are removed from messenger RNA (mRNA) precursor molecules. Most genes contain introns that are transcribed into the pre-mRNA but need to be removed. The splicing process involves two reactions in the spliceosome, a complex of RNA and proteins, that cuts out the intron and joins the exons to produce mature mRNA that can then be translated into protein. Alternative splicing allows one gene to encode multiple proteins through differential splicing of exons.