Embed presentation
Downloaded 11 times


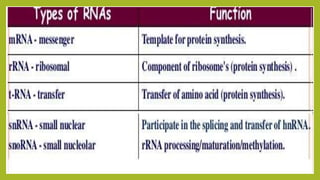





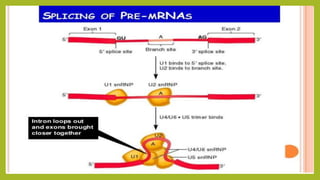
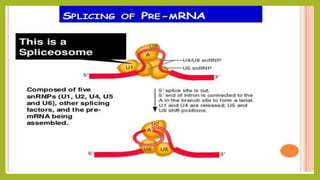
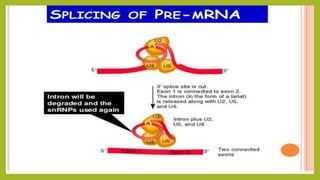

RNA splicing is the process where introns are removed and exons are joined together to form mature mRNA. It occurs in the nucleus and involves two main types: self-splicing, where the intron splices itself, and spliceosome-mediated splicing, which uses small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) containing small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) and proteins. The five major snRNPs involved in spliceosome-mediated splicing are U1, U2, U4, U5, and U6.











