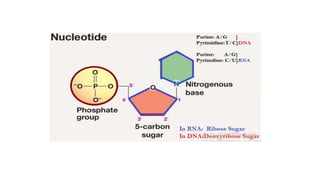
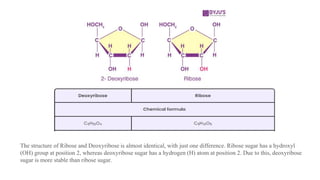
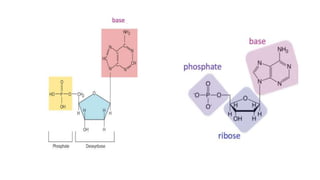
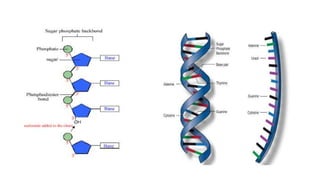
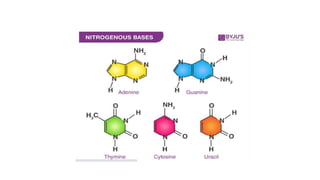
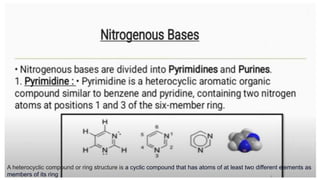
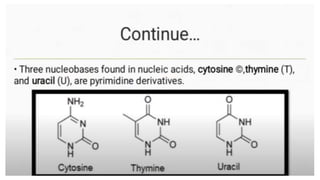
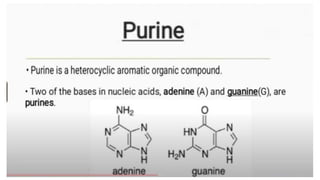
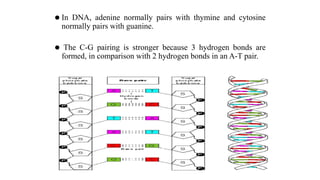
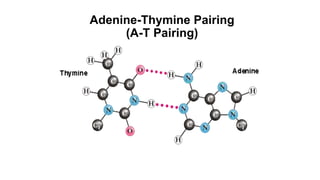
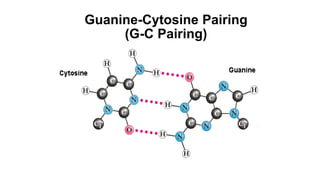
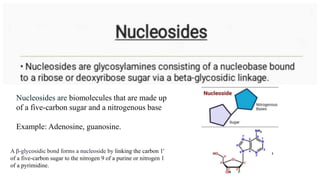
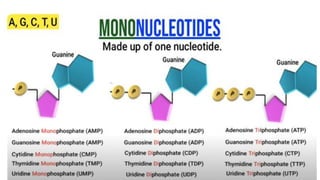
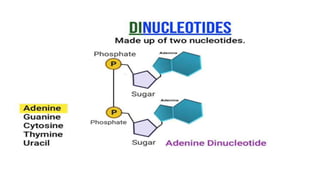
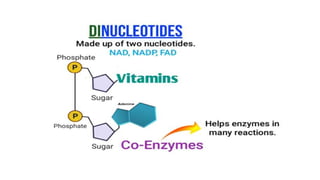
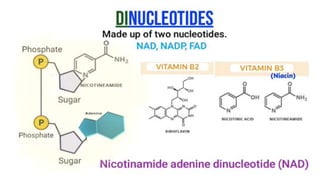
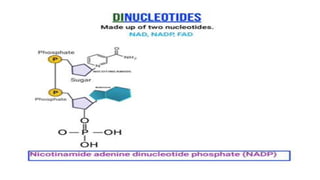
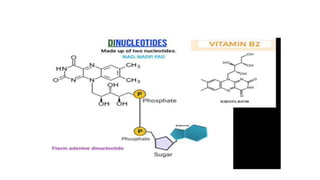
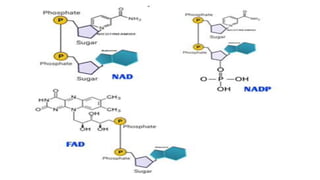
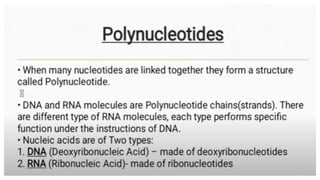
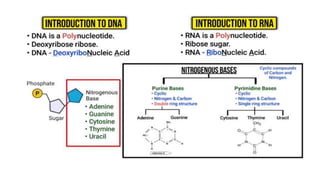
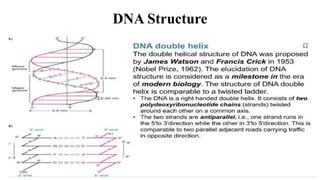
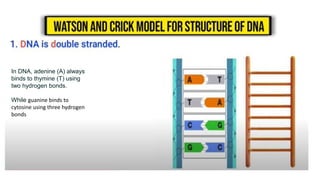
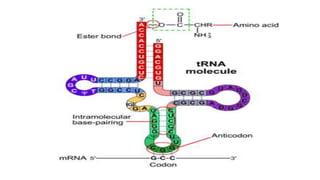
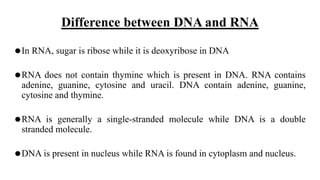
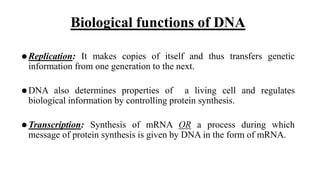
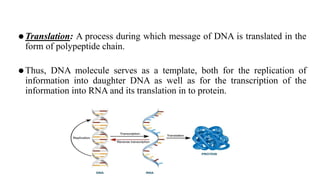
This document discusses the structural differences between ribose and deoxyribose sugars, highlighting that deoxyribose is more stable. It explains the pairing of nitrogenous bases in DNA and RNA, detailing the roles of messenger RNA, transfer RNA, and ribosomal RNA in protein synthesis. Additionally, it outlines the biological functions of DNA including replication, transcription, and translation.