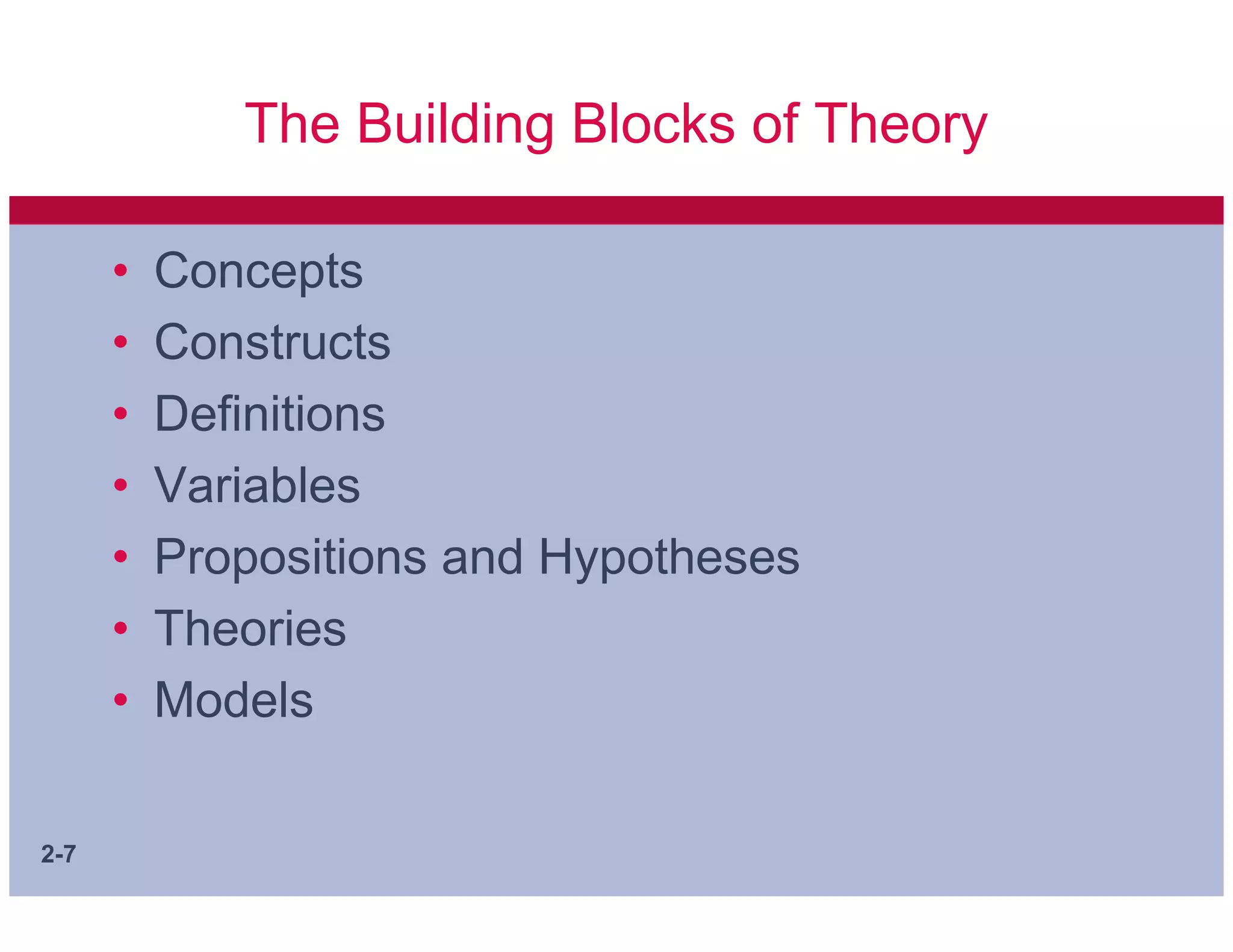
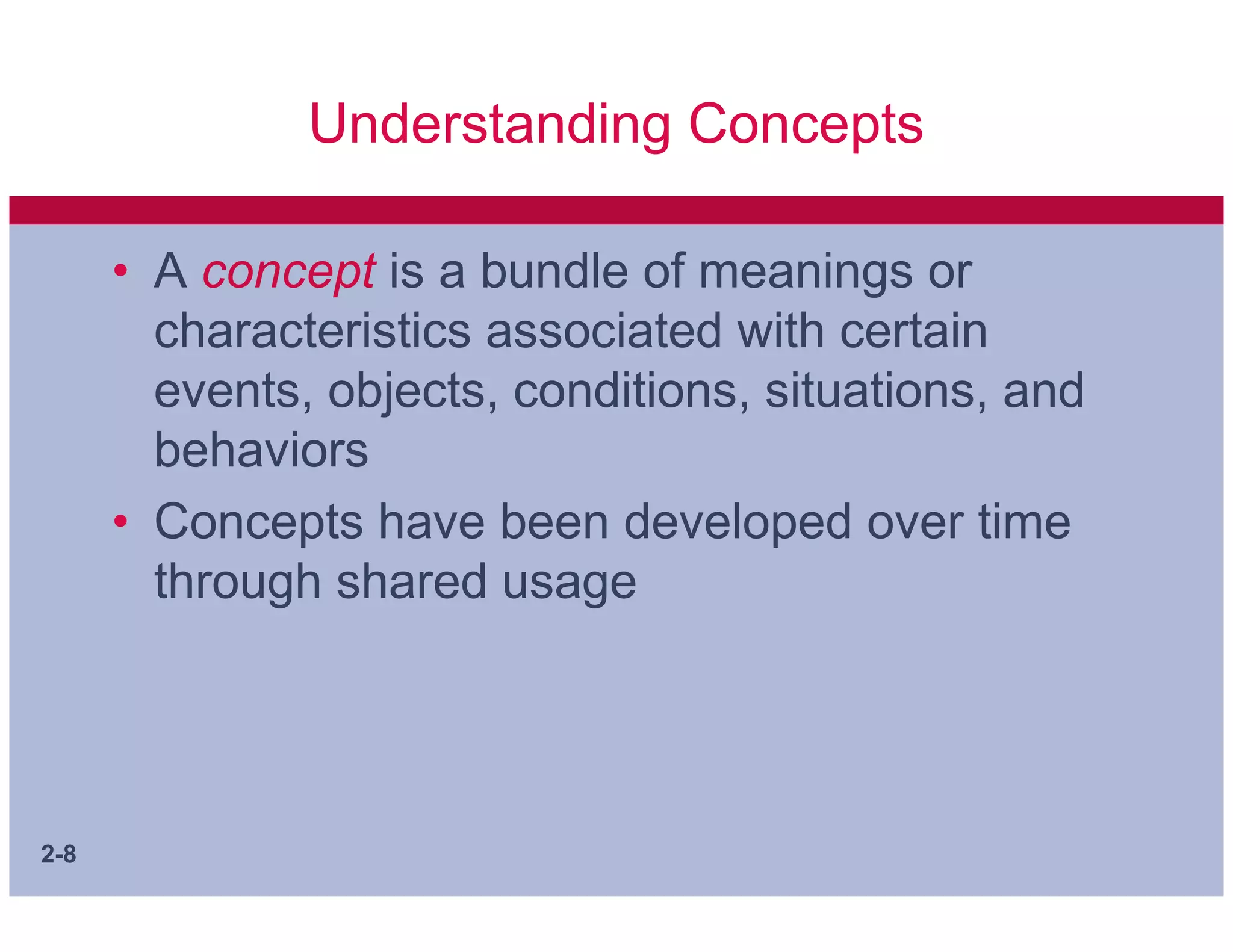
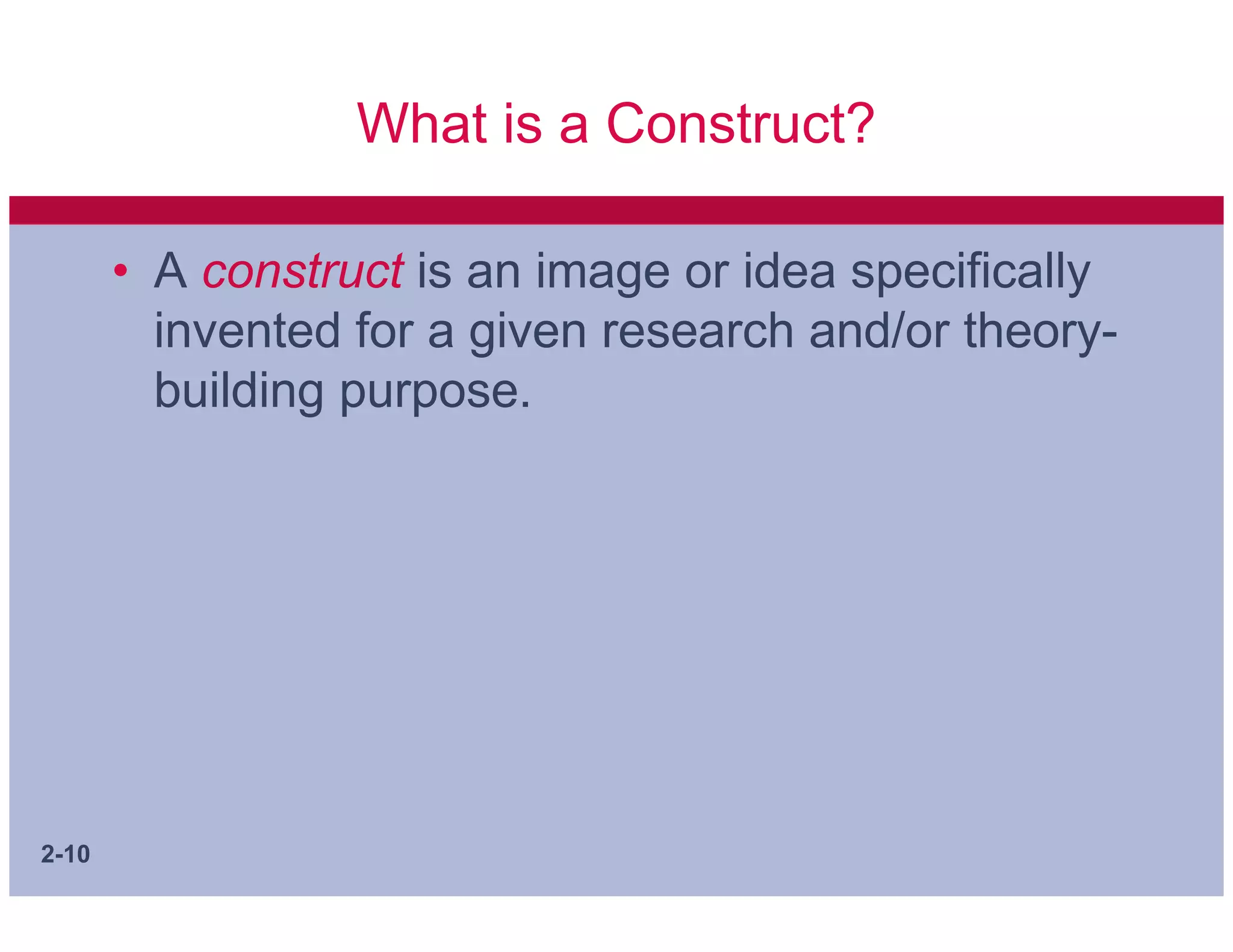
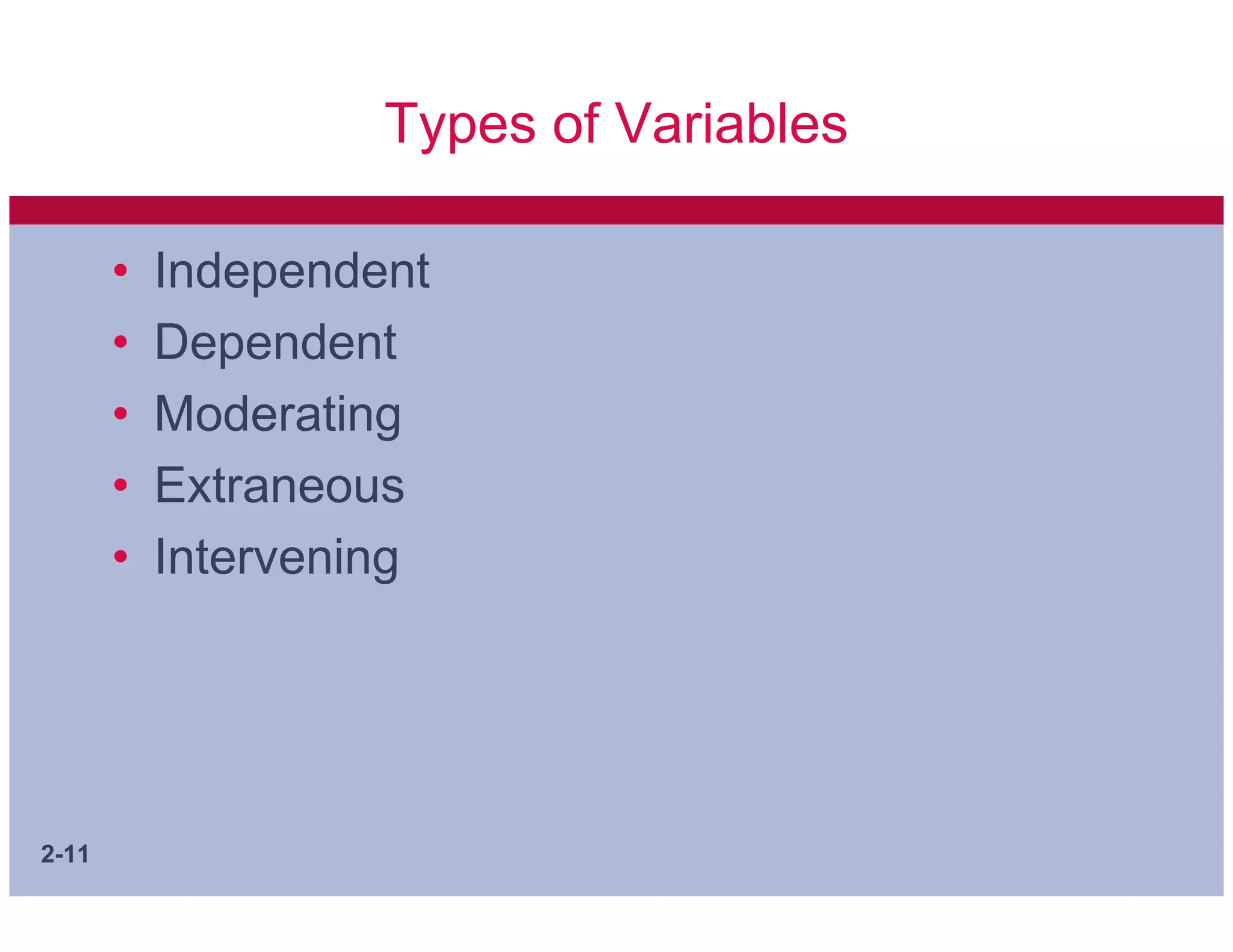
This document discusses key concepts in applying scientific thinking to management problems. It covers sources of knowledge, the essential tenets of science, ways to communicate arguments, and important building blocks of theory such as concepts, constructs, variables, hypotheses, theories, and models. A good hypothesis should be adequate for its purpose, testable, and better than alternative hypotheses. Developing clear concepts and theories helps structure research and identify meaningful facts to study.