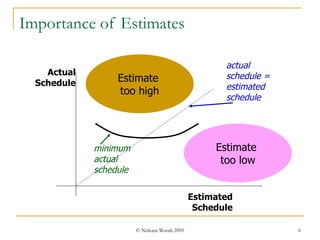
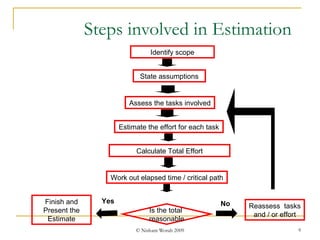
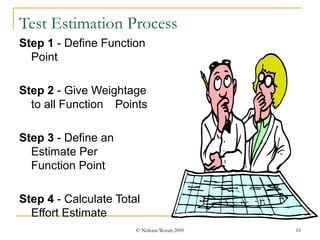
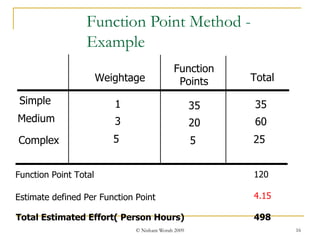
Test estimation involves forecasting the time and costs required using techniques like function point analysis. It is important as underestimating can lead to budget overruns and delays. The key steps are: 1) Define functionality using use cases or test cases; 2) Assign weights to complexity; 3) Estimate effort per point; and 4) Calculate total effort. Allowing time for proper estimation, using past project data, and re-estimating throughout the project lifecycle can improve accuracy. Regular communication of assumptions and estimates is also important.