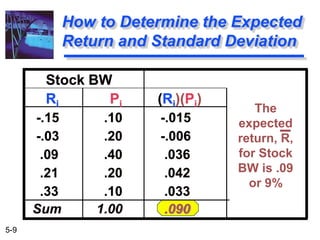
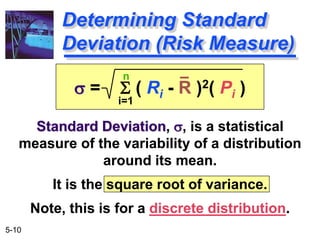
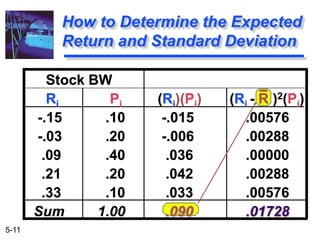
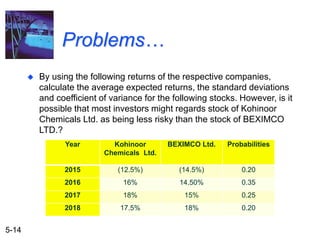
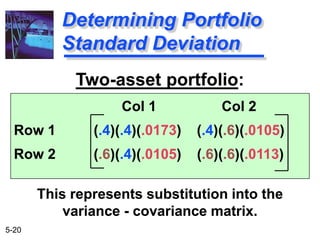
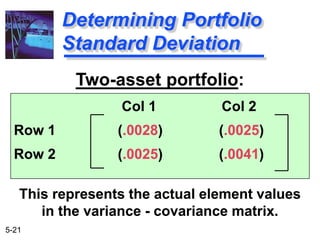
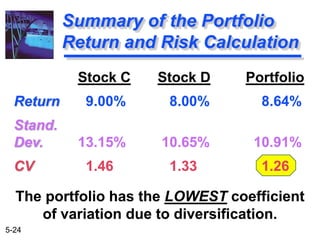
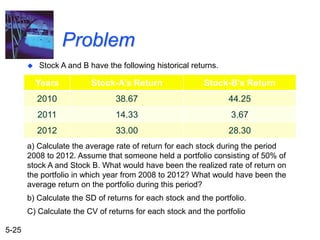
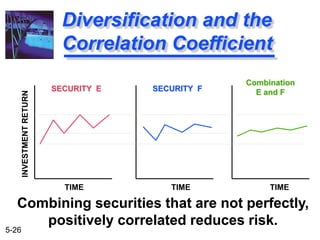
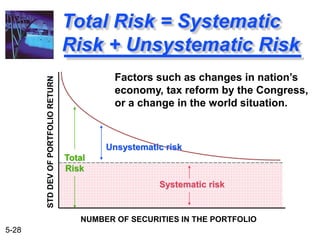
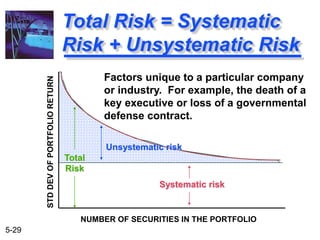
The document explains the concepts of risk and return in investment, detailing how to measure them through expected return, standard deviation, and coefficient of variation. It differentiates between avoidable (unsystematic) and unavoidable (systematic) risks and emphasizes the importance of diversification in managing these risks. Additionally, it covers portfolio management techniques, including calculations for expected return and standard deviation for different portfolio compositions.