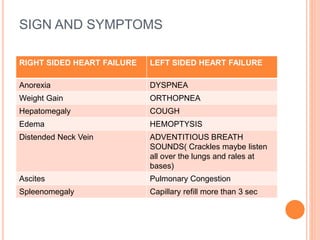
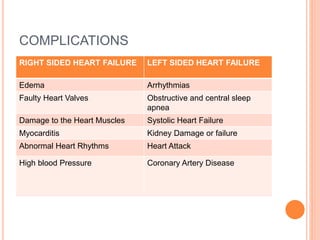
This document discusses right and left sided heart failure. Right sided heart failure affects the right side of the heart which collects deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps it to the lungs. Left sided heart failure affects the left side which pumps oxygenated blood from the lungs to the rest of the body. It describes the signs, symptoms, complications, causes, nursing management, medical management including medications like beta blockers and diuretics, and surgical options for treating heart failure.