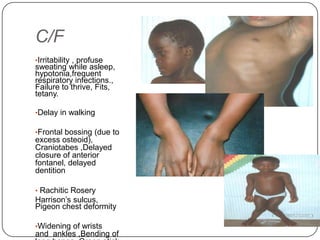
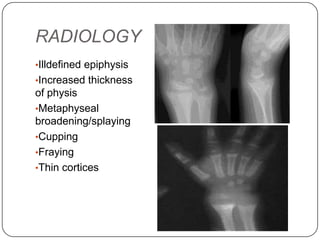
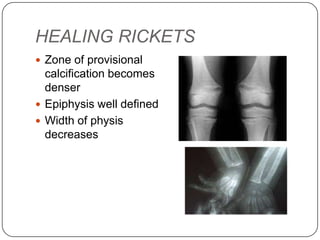
Rickets and osteomalacia are disorders caused by interrupted mineralization of bone due to calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D metabolism issues. Rickets occurs in children and causes bone deformities, while osteomalacia occurs in adults. Various types of rickets include vitamin D deficiency, vitamin D dependent, and vitamin D resistant. Treatment involves vitamin D supplementation, calcium supplementation, and correcting fluid and electrolyte imbalances. Osteomalacia in adults is also caused by vitamin D deficiency and is treated with vitamin D supplementation.