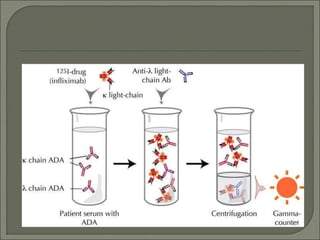
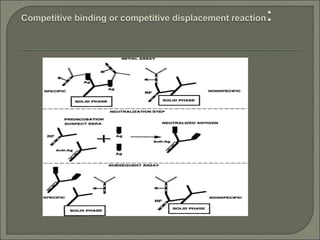
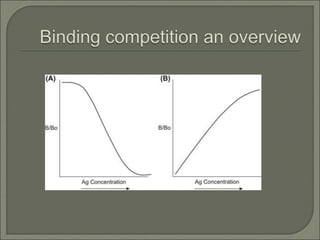
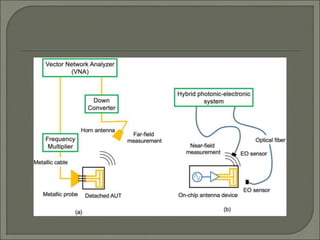
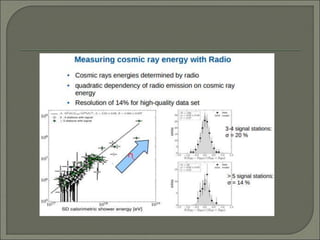
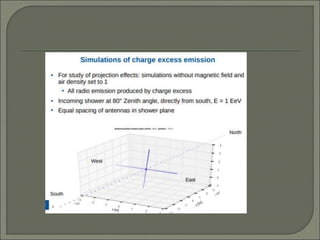
Radioimmunoassay (RIA) is an in vitro assay that uses radioisotopes conjugated to antigens or antibodies to detect antigen-antibody complexes with high sensitivity. RIA involves an antigen-antibody immune reaction, competitive binding between labeled and unlabeled antigens for antibodies, and measurement of radio emissions. The amount of unlabeled antigen in a sample can be determined based on the amount of labeled antigen displaced from antibodies. RIA allows for quantification of very small quantities of antigens and antibodies and is used to analyze concentrations of hormones, drugs, and viral antigens in biological fluids.