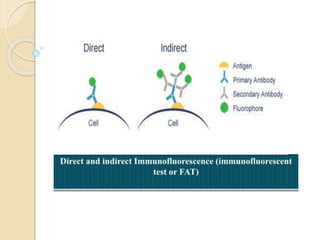
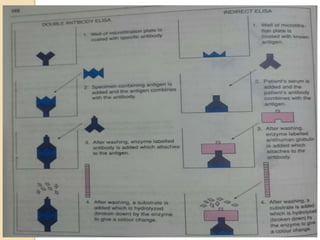
The document discusses various types of antigen-antibody reactions:
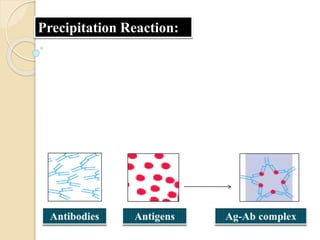
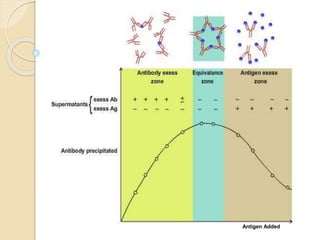
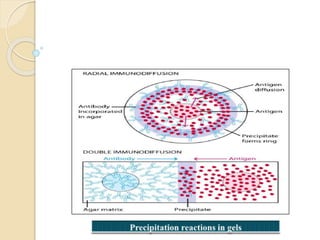
1) Precipitation reactions occur when antigen is mixed with antibodies.
2) Agglutination reactions cause particulate antigens to clump together when mixed with antibodies in the presence of electrolytes. Common examples are blood grouping and detection of typhoid.
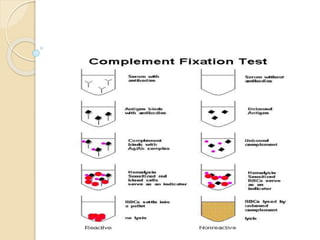
3) Neutralization reactions involve antitoxins neutralizing toxins. Examples include toxigenicity tests and the Schick test.