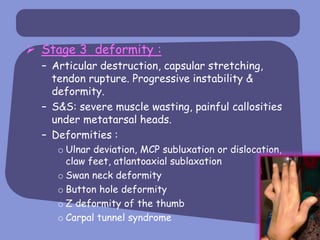
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the joints, causing swelling and stiffness, eventually resulting in deterioration of bone and cartilage. It is caused by an autoimmune response and is characterized by symmetric inflammation of multiple small joints of the hands and feet. Symptoms progress from early inflammation to joint destruction and deformity if left untreated.