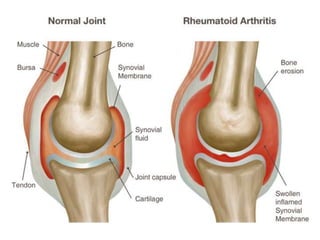
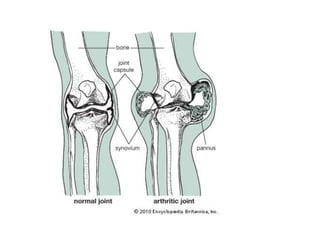
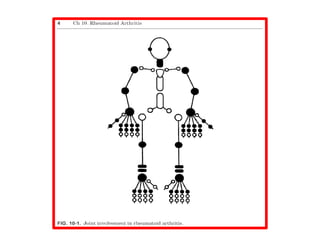
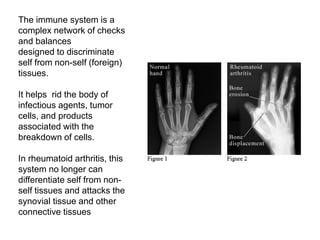
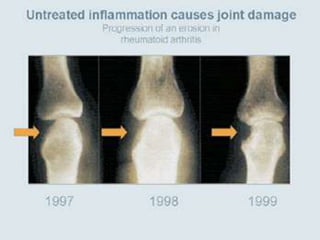
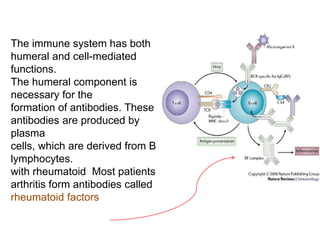
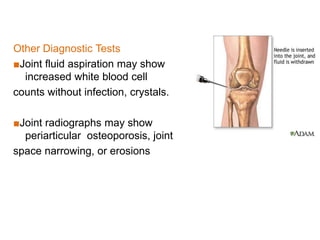
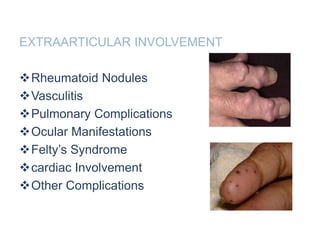
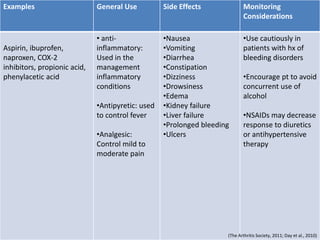
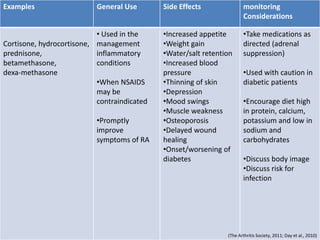
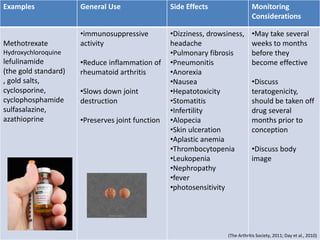
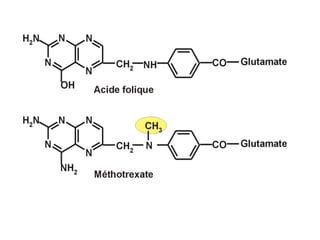
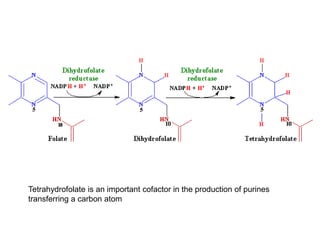
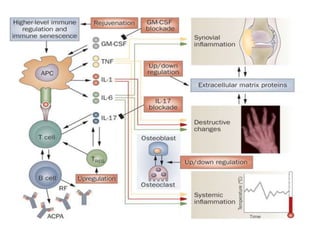
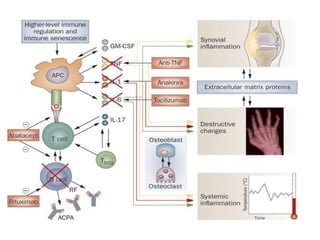
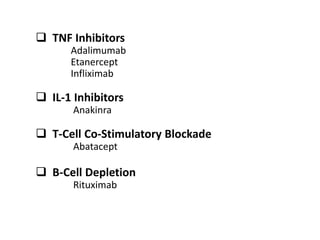
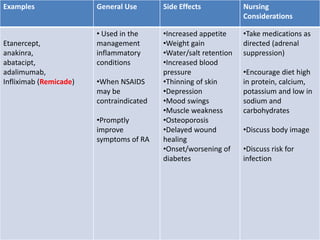
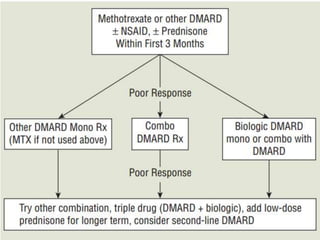
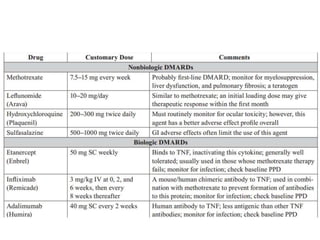
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. It affects around 1-2% of the population, most often women. Treatment involves controlling inflammation to slow disease progression and manage symptoms. This is achieved through a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapies including NSAIDs, corticosteroids, DMARDs, biologics, exercise, and assistive devices. The goal of treatment is reduced joint tenderness, swelling and pain as well as improved quality of life. Careful monitoring is required due to potential adverse effects of long-term drug therapy.