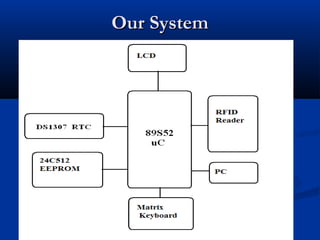
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is an automatic identification technology that uses RF signals to identify and track objects, people, or animals via RFID tags. These tags can be passive, semi-passive, or active, and they require an RFID reader to function, which converts the signals from the tags for data processing. RFID technology has various applications including access control, asset management, mass transit ticketing, and monitoring systems, and it offers benefits such as affordability and portability.