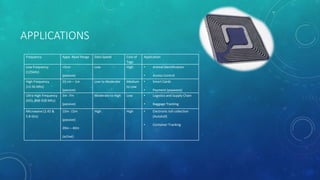
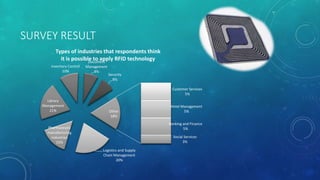
This document discusses RFID (radio frequency identification) technology, its components, types of tags, and applications. It provides details on passive, semi-passive, and active tags and their read ranges. Common applications mentioned include credit cards, transportation payment systems, toll collection, access control, and supply chain management. The document also summarizes an online survey of possible RFID applications and its results. Further development opportunities in medical and library uses are noted, along with positives and negatives of the technology.