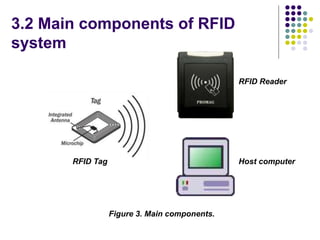
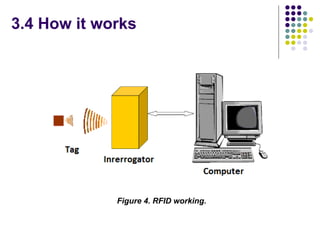
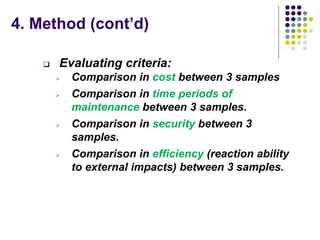
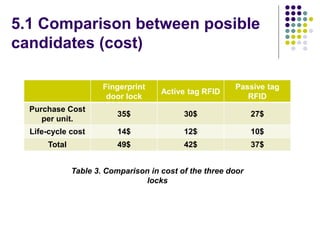
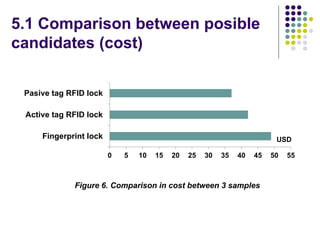
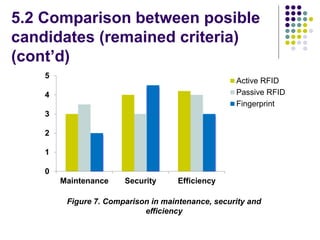
The document evaluates proposals from three companies for an RFID door lock system for a bank building. It analyzes the proposals based on cost, maintenance, security, and efficiency. The evaluation finds that the active RFID system best meets the criteria, being more secure and efficient while still affordable. It is recommended to purchase the active RFID locks to ensure safety of employees and property within the budget.