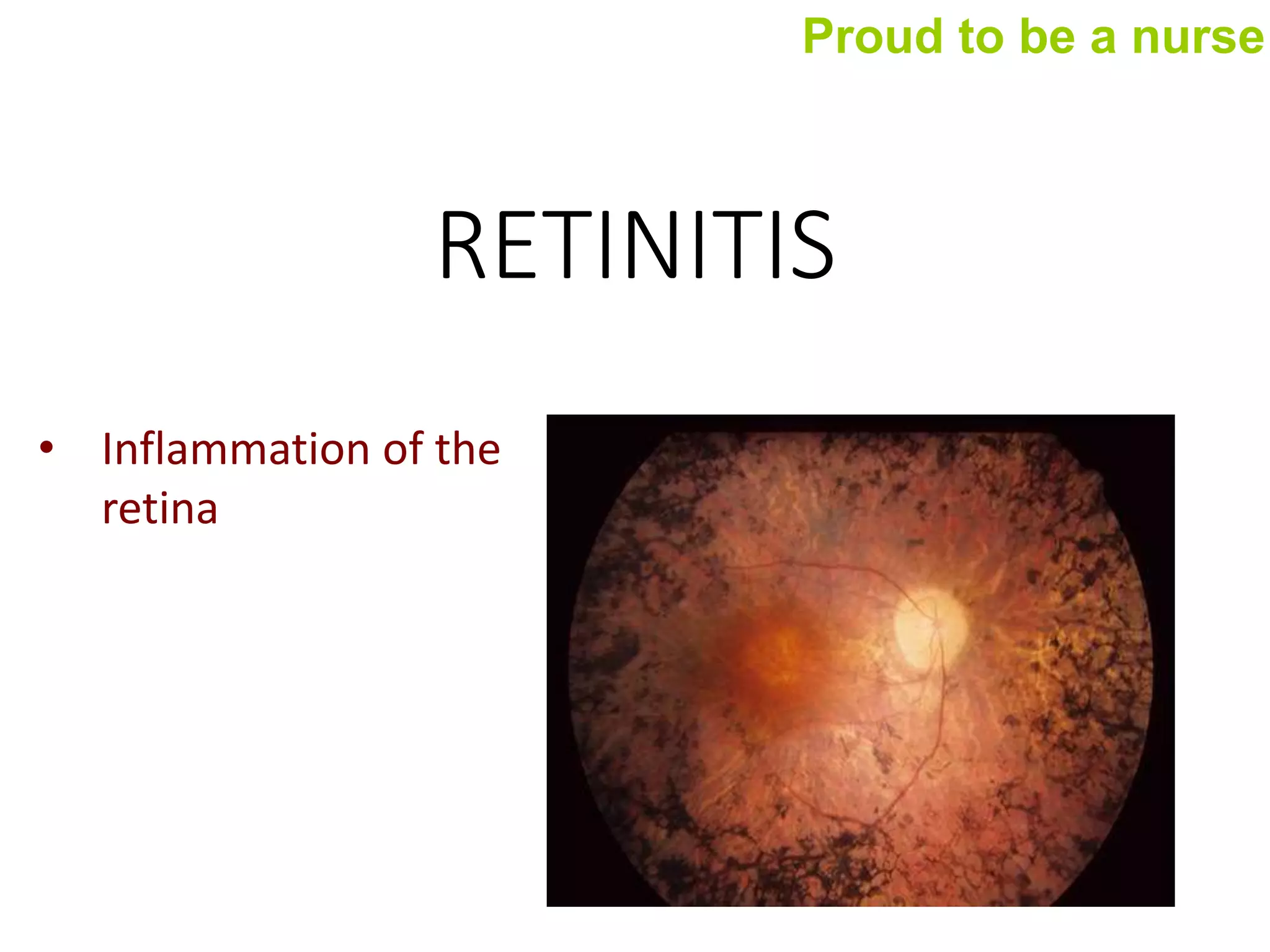
Retinitis is inflammation of the retina that can be caused by various pathogens like toxoplasma, cytomegalovirus, and herpes zoster virus. There are different types of retinitis including retinitis pigmentosa, which is a genetic eye disease that affects night vision. Clinical manifestations include blurred vision, loss of side vision, floaters, and tunnel vision. Diagnostic tests include eye examinations, visual field testing, genetic testing, and imaging tests like OCT. Management involves pharmacological treatments like carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and lutein, as well as surgical options like bionic retinas and retinal transplantation. Nursing management focuses on pain management, maintaining visual function, and preventing injury related to impaired vision.