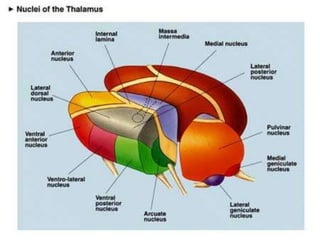
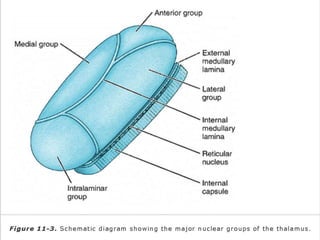
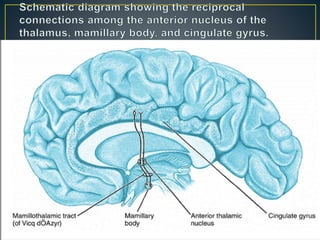
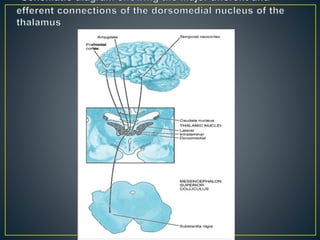
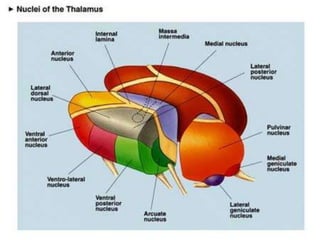
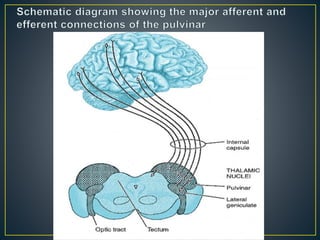
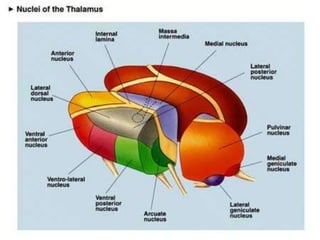
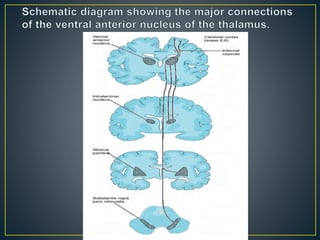
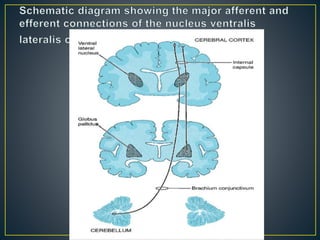
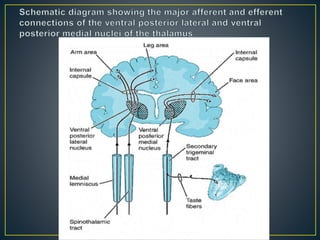
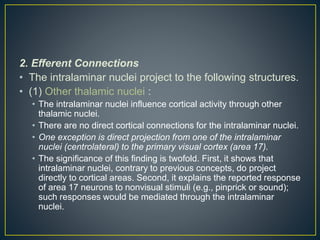
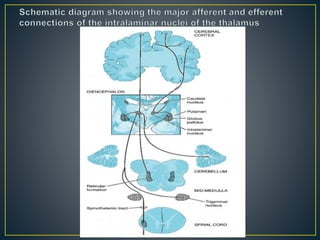
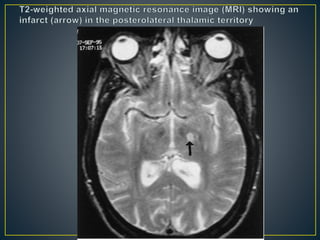
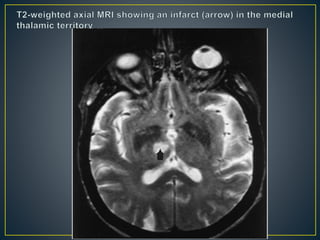
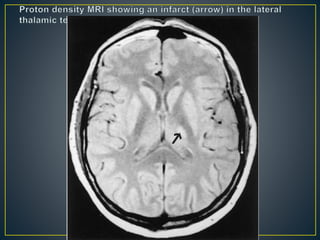
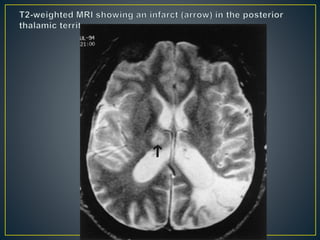
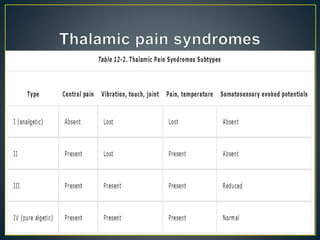
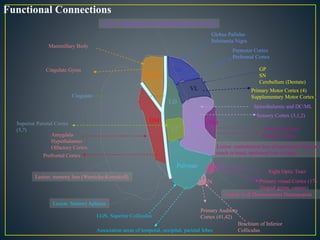
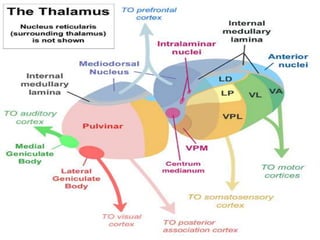
The thalamus is a large structure in the diencephalon that serves as a relay center between various brain regions. It is subdivided into several nuclear groups including anterior, medial, lateral, intralaminar and reticular nuclei. The thalamus receives sensory information from ascending tracts and projects to different areas of the cerebral cortex, playing roles in motor, sensory, cognitive and limbic functions. Specific thalamic nuclei have reciprocal connections with cortical and subcortical regions to integrate various neural systems.