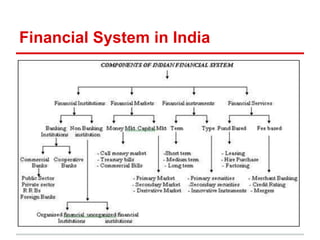
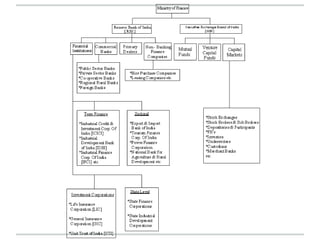
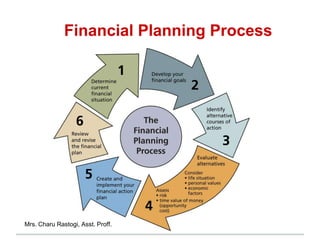
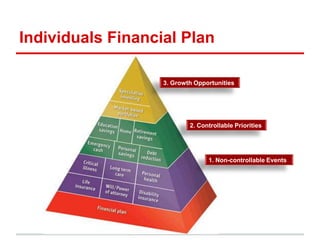
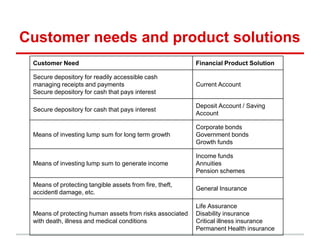
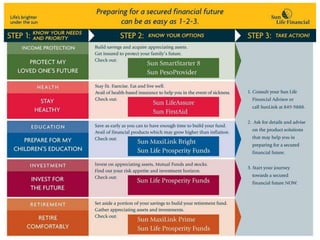
The document outlines financial products and services, detailing their definitions, functions, and classifications within the Indian financial system. It discusses the management of financial products through planning processes aimed at meeting individual financial goals, such as investment strategies, risk management, and the provision of financial advice. Additionally, it highlights various categories of financial instruments and the roles of financial institutions and markets in facilitating economic development.