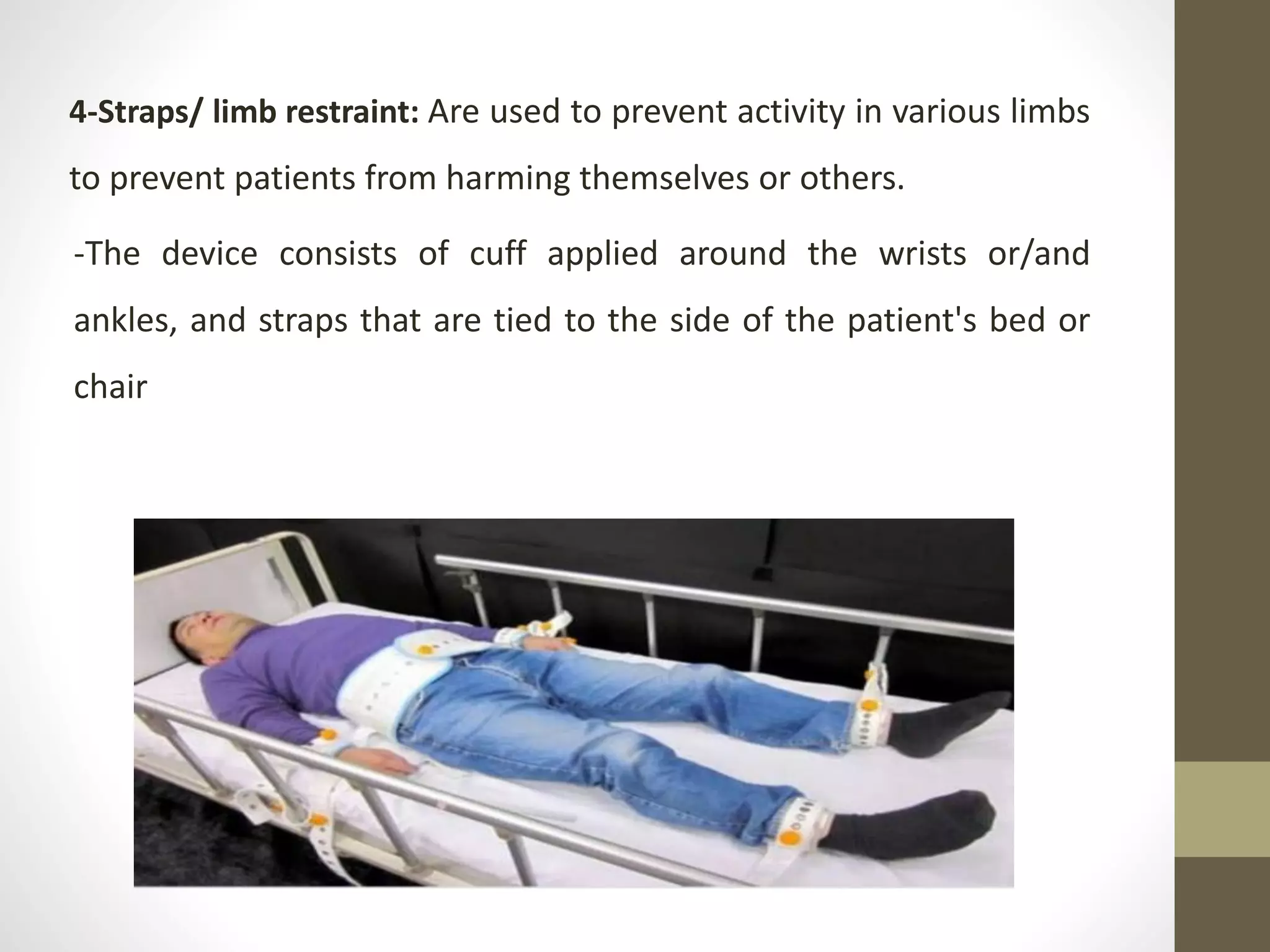
This document defines restraint and seclusion, outlines their indications and contraindications, and describes different types of restraints and seclusion rooms. It defines restraint as involuntary control through chemical or mechanical means to prevent harm, and seclusion as involuntary confinement in a locked room where the person can be observed. The least restrictive methods like reducing stimuli, verbal intervention, and meeting needs should be tried first before restraint or seclusion.