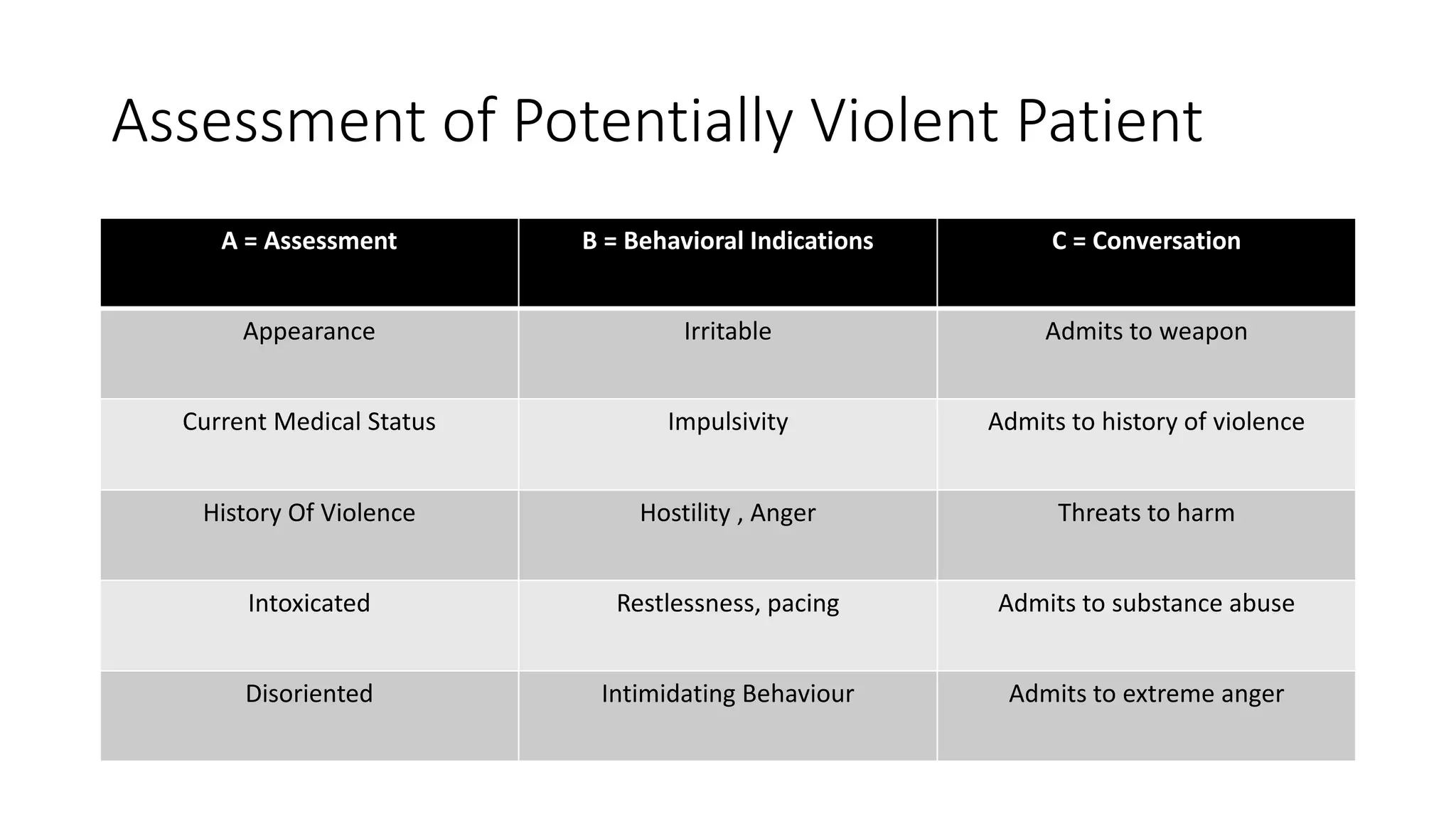
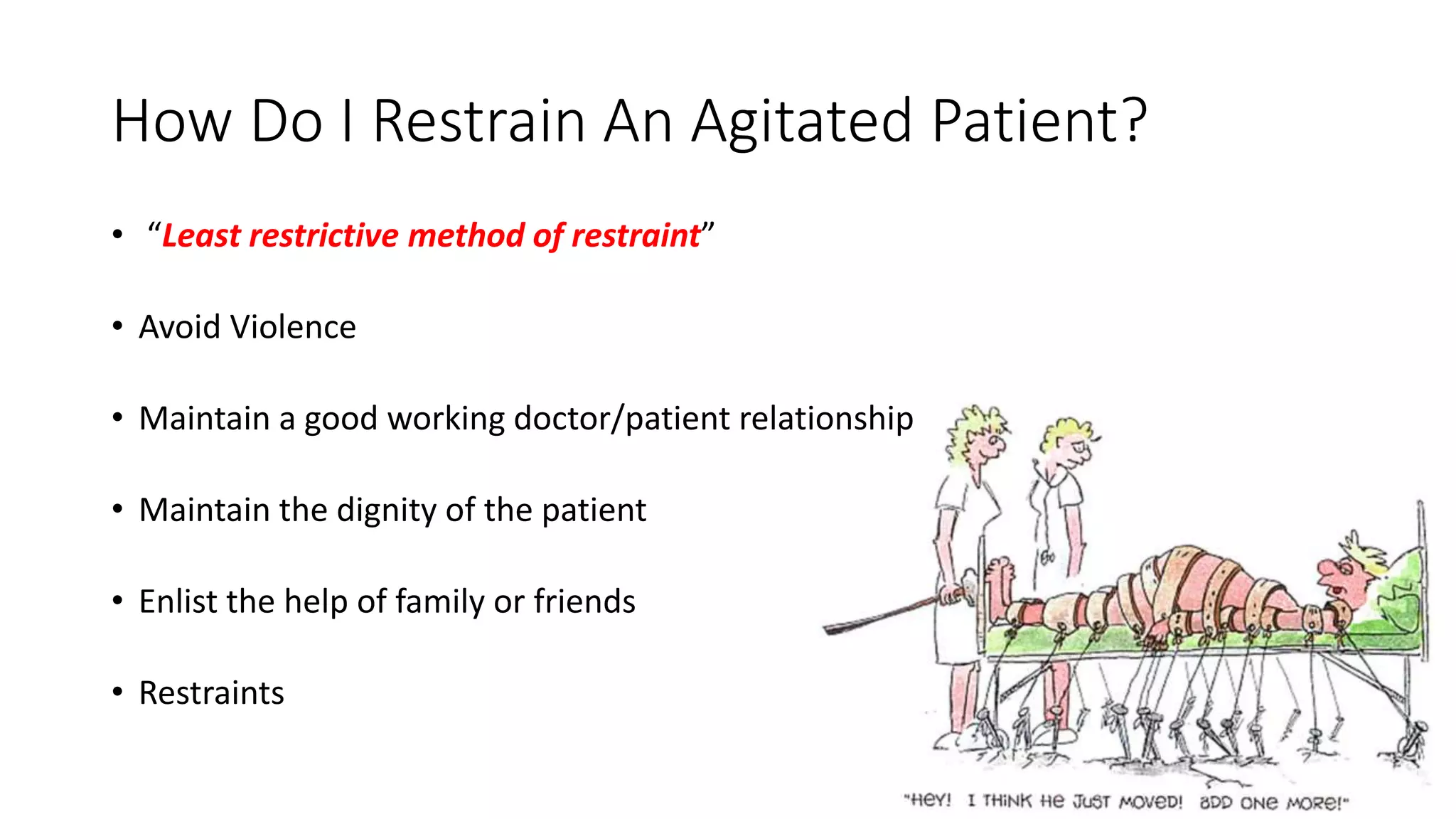
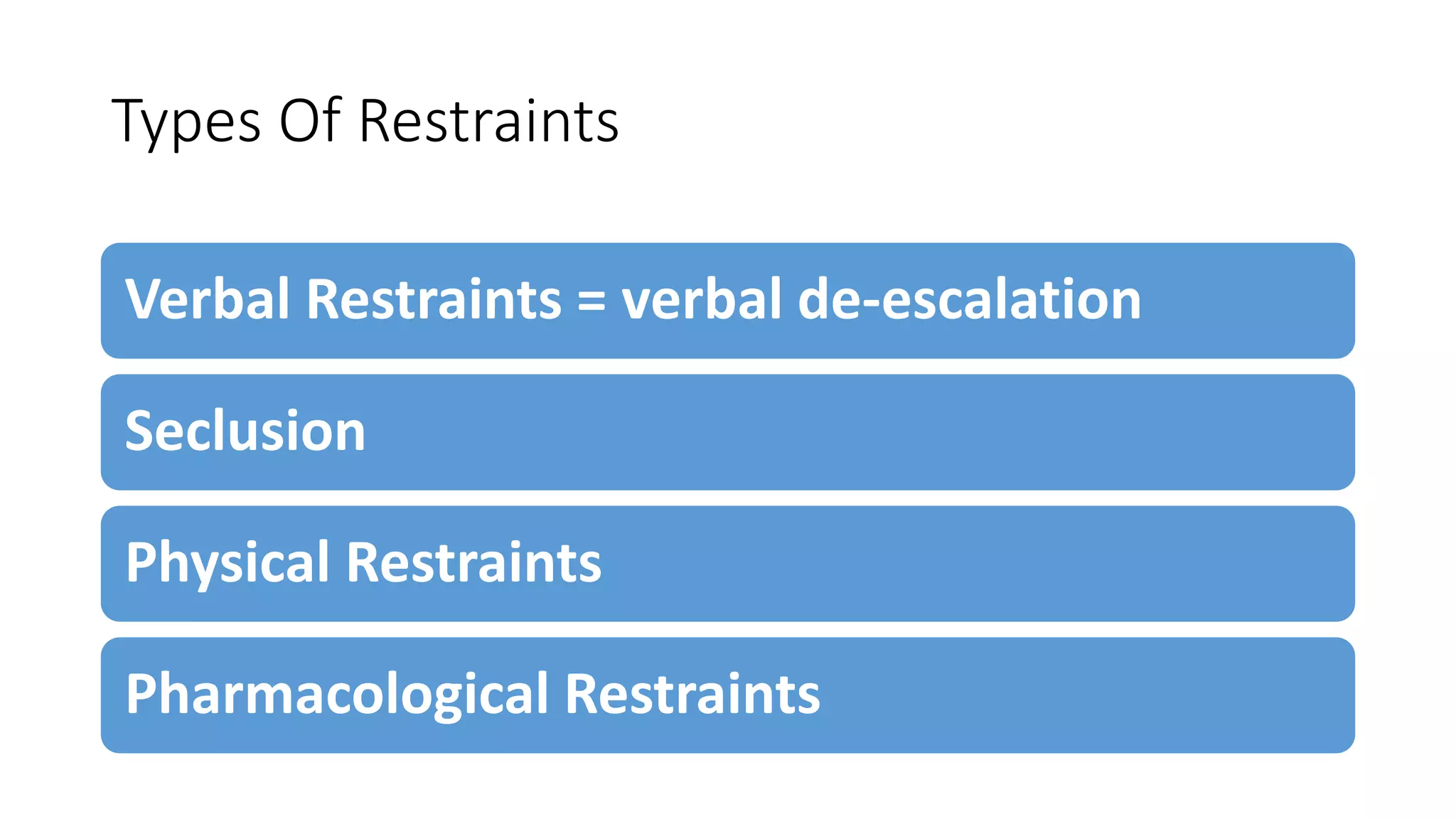
The document discusses the assessment and management of agitated patients who may need to be placed in restraints. It provides guidance on:
1) Who should be restrained, including those who are a danger to themselves or others due to medical conditions, intoxication, or psychiatric disorders.
2) Why restraints should be used - to protect medical staff, the patient, and allow for proper assessment and treatment. The least restrictive methods should be attempted first.
3) The different types of restraints that can be used including verbal de-escalation, seclusion, physical restraints, and chemical restraints using medications like haloperidol or lorazepam. Proper documentation of the restraint procedure