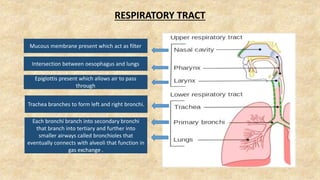
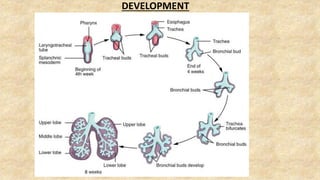
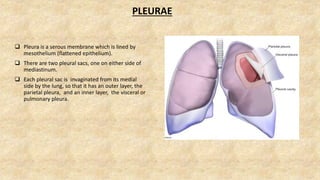
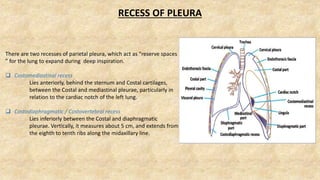
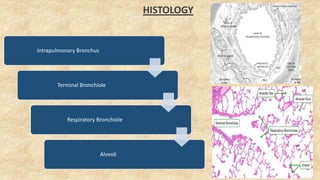
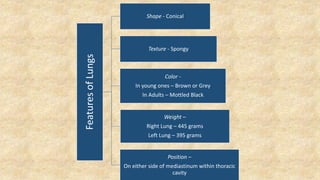
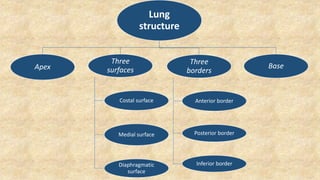
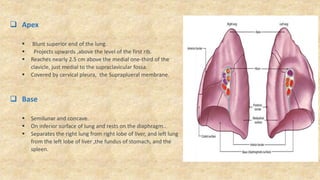
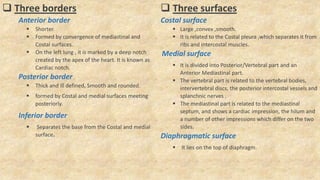
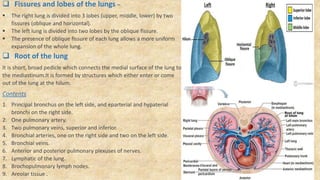
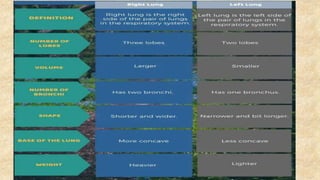
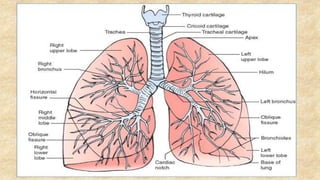
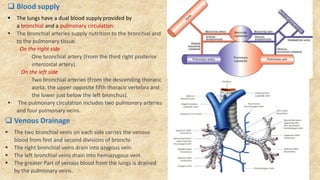
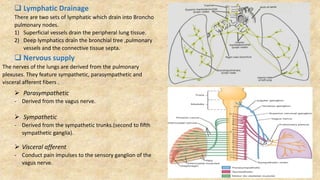
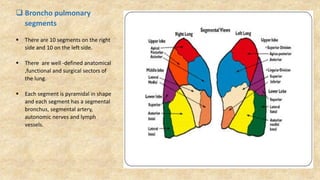
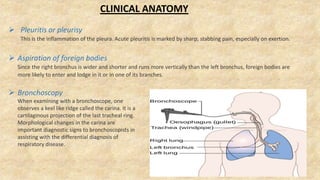
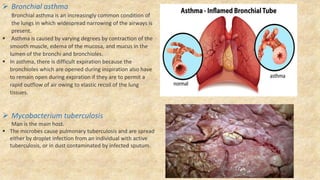
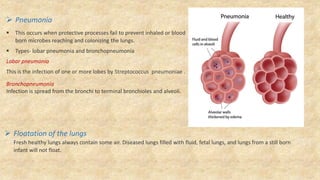
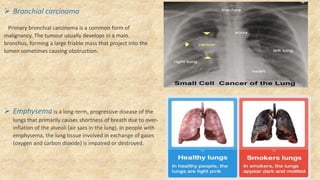
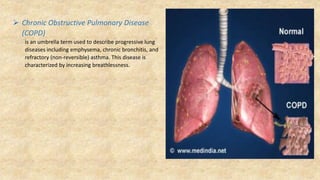
The document summarizes key aspects of respiratory anatomy and physiology. It describes the structure and function of the lungs, including details on lobes and fissures, vascular and lymphatic supply, innervation and development. It also discusses common respiratory diseases and clinical relevance of respiratory anatomy, such as in bronchoscopy, pneumonia, tuberculosis, asthma and lung cancer.