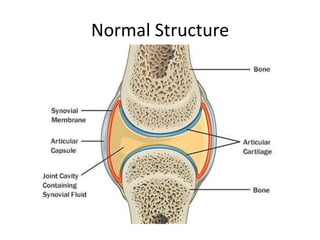
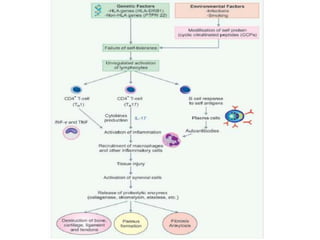
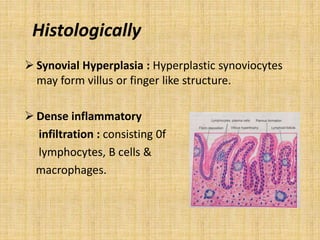
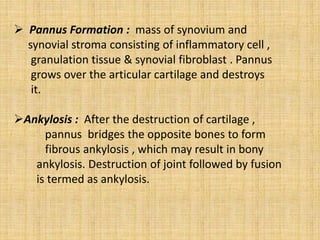
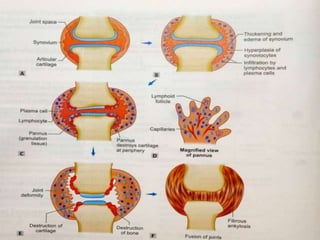
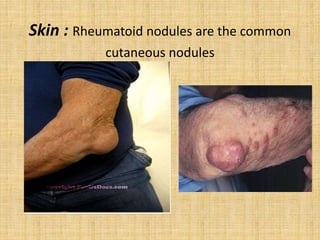
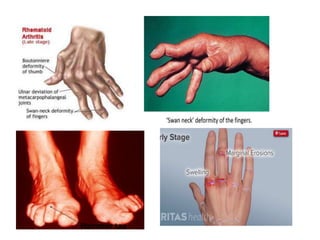
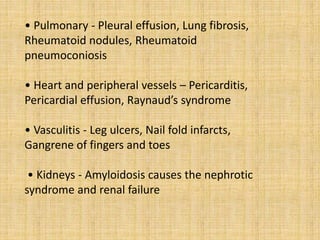
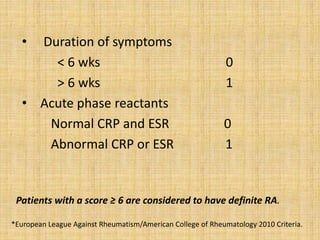
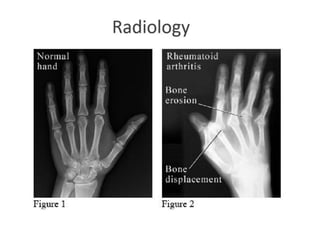
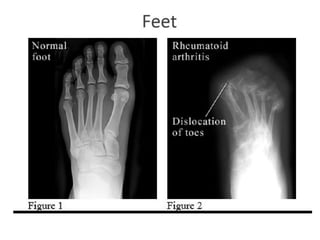
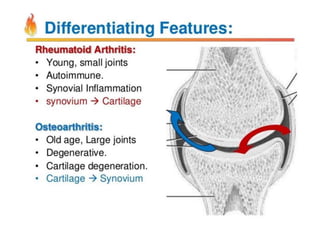
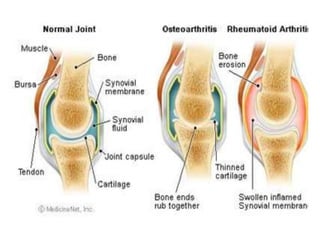
This document provides an overview of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), including its epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnostic criteria, and management. RA is a chronic autoimmune disorder causing symmetrical polyarthritis, most commonly affecting the small joints of the hands and feet. It results from a breakdown of self-tolerance and cytokine-mediated inflammation that leads to joint destruction. Diagnosis is based on symptoms, serology tests, and x-ray findings. Treatment involves NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and disease-modifying drugs to suppress symptoms and prevent long-term joint damage.