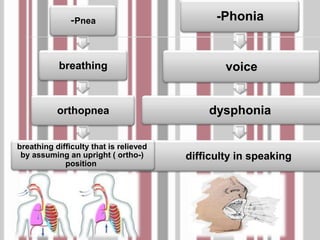
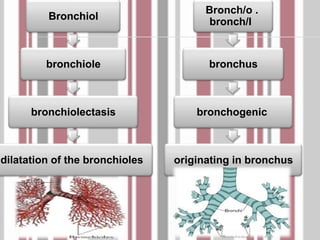
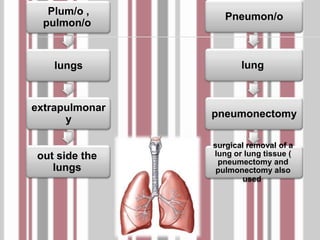
The document discusses the respiratory system and common respiratory diseases. It defines key terms related to breathing and lung function. Some common lung diseases mentioned include cystic fibrosis, asthma, emphysema, pneumonia, and tuberculosis. It also describes how doctors use a spirometer to test lung function and diagnose conditions like asthma and cystic fibrosis.

























![is a common chronic inflammatory disease of
the airways characterized by variable and
recurring symptoms, reversible airflow
obstruction, and bronchospasm.[2] Common
symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest
tightness, and shortness of breath.[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/respiratorysystem-130414181813-phpapp01/85/Respiratory-system-29-320.jpg)








