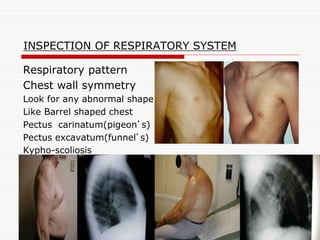
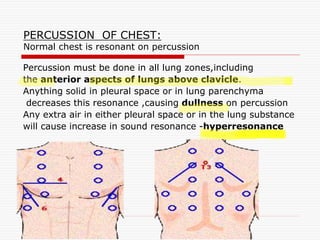
This document provides an overview of examining the respiratory system. It discusses common symptoms like cough, dyspnea, and hemoptysis. For cough, it describes different types and potential causes like acute or chronic bronchitis, asthma, and GERD. For dyspnea, it discusses grades and positions as well as acute and chronic causes. Hemoptysis expectoration is examined based on amount and potential causes in the airways, vasculature, or parenchyma. The physical exam of the respiratory system is outlined, including inspection of breathing patterns, percussion notes, tactile fremitus, and auscultation of breath sounds.