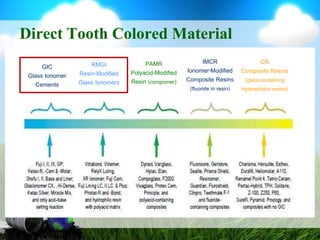
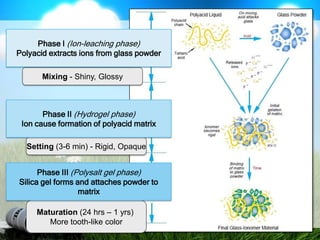
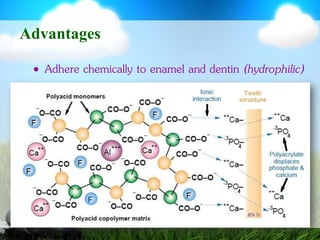
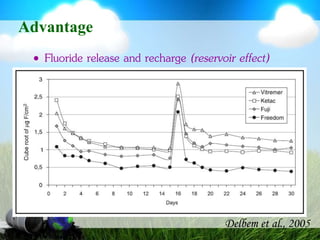
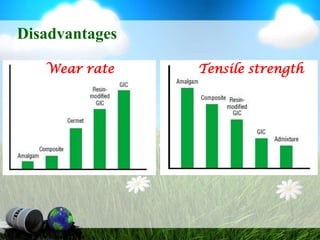
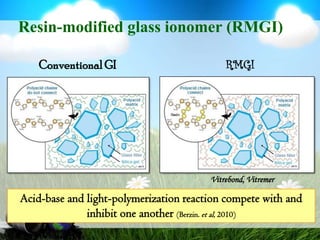
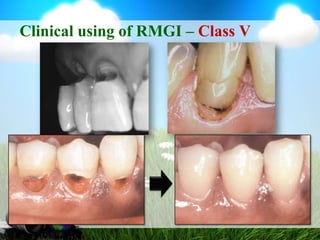
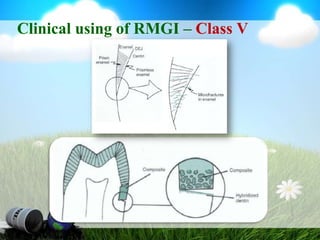
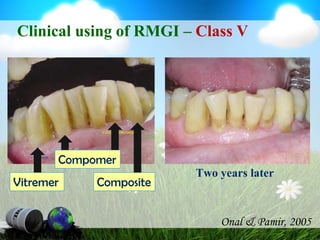
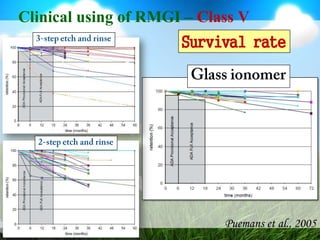
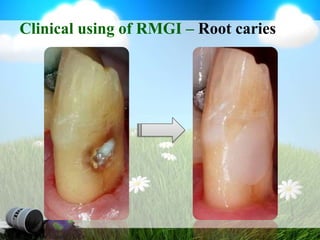
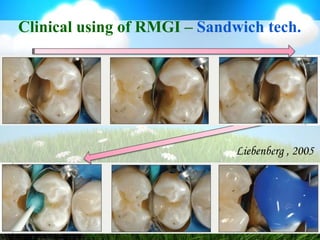
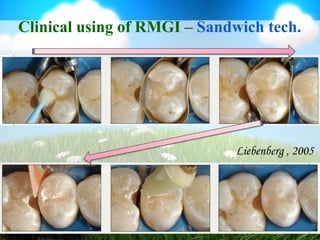
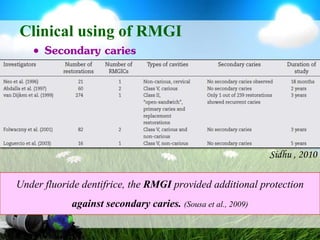
This document discusses glass ionomer cement and resin-modified glass ionomer cement in restorative dentistry. It describes the composition and setting reactions of glass ionomer cement, as well as its advantages like adhesion to tooth structure, fluoride release, and low shrinkage. However, it also notes disadvantages like poorer wear resistance and physical properties compared to resin composites, as well as ongoing moisture sensitivity issues. The document then discusses how resin-modified glass ionomer cements were developed to improve properties like strength and reduce moisture sensitivity issues. It concludes by describing clinical applications of resin-modified glass ionomer cements, such as for class V restorations, root caries treatment, and the sandwich technique.