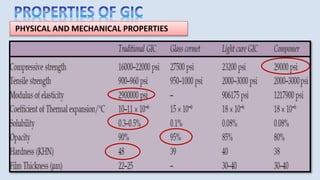
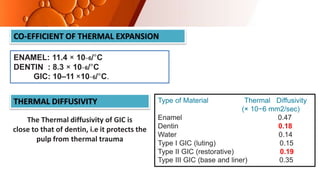
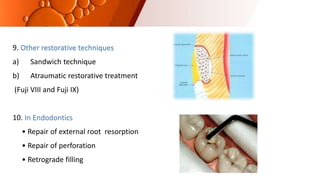
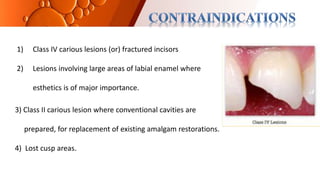
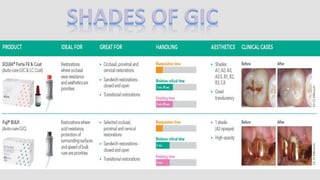
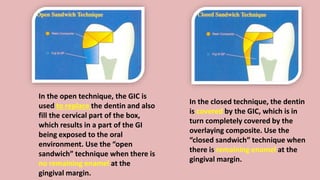
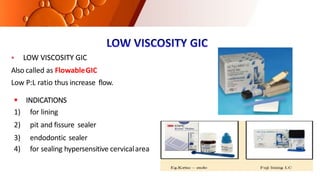
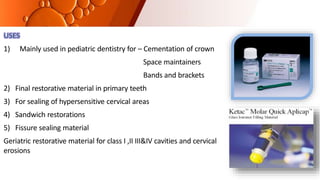
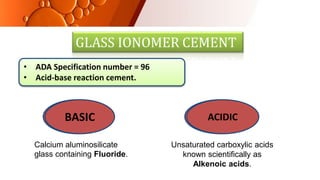
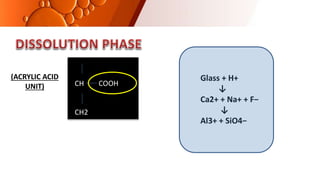
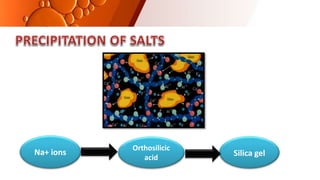
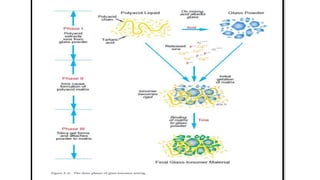
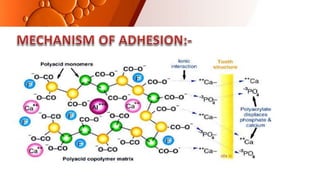
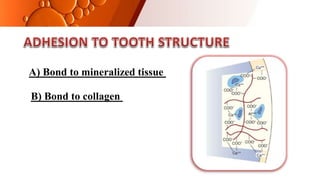
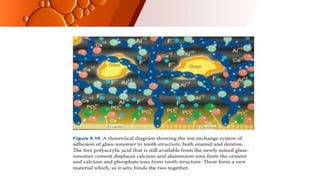
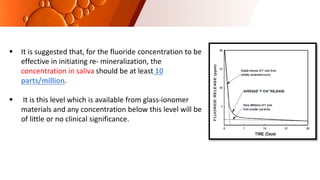
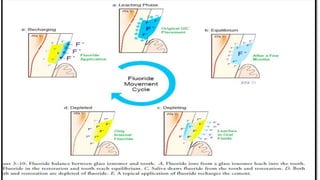
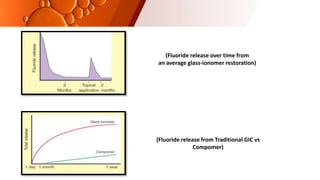
The document provides an overview of glass ionomer cement (GIC), including its history, composition, properties, applications, and advances. It discusses how GIC sets via an acid-base reaction between glass powder and polyacrylic acid liquid. Key points include that GIC bonds chemically to tooth structure, has coefficient of thermal expansion similar to tooth, and provides long-term fluoride release for remineralization. The document also reviews classifications of GIC, advantages like adhesion and fluoride release, and limitations like moisture sensitivity. Finally, it discusses newer GIC formulations like resin-modified, metal-reinforced, and polyacid-modified GICs that aim to improve properties.
















![CEMENT TYPE 14 DAYS 30 DAYS
CERMET 200 µg 300 µg
SILVER ALLOY ADMIX 3350 µg 4040 µg
TYPE I GIC 470 µg 700 µg
TYPE II GIC 440 µg 650 µg
GIC LINER [conventional] 1000 µg 1300 µg
GIC LINER [Light cure] 1200 µg 1600 µg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gic-231221142904-df7a0b8d/85/GIC-pptx-conservative-dentistry-and-endodontics-33-320.jpg)