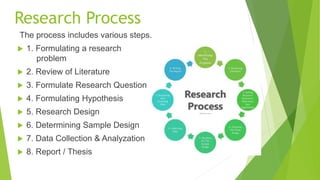
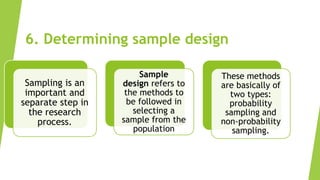
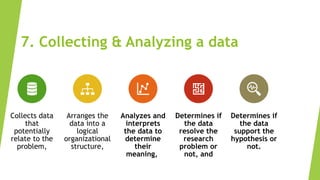
The research process involves multiple steps, including formulating a research problem, reviewing relevant literature, formulating research questions and hypotheses, designing the research methodology, determining sampling methods, collecting and analyzing data, and reporting findings. It begins with identifying an interesting research problem and topic. The researcher then reviews existing literature to learn what is already known and not known about the topic to help narrow the research question. Next, the researcher develops a research design and sampling method to collect and analyze data to address the research question and test any hypotheses. Finally, the researcher prepares a report summarizing the full research process and findings.