1. The document discusses common pitfalls in research studies related to reproductive medicine and how to avoid them.
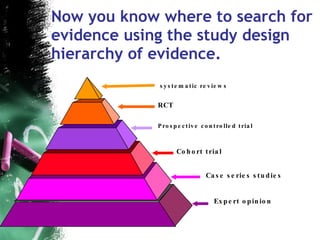
2. Key pitfalls include problems with study design, sampling, operationalization, and generalizability. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are recommended to properly assess treatment efficacy.
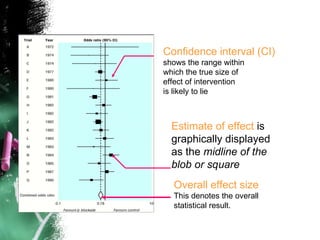
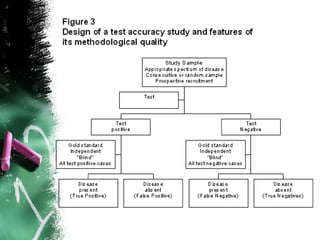
3. When conducting RCTs, intention-to-treat analysis and accounting for loss to follow up are important to avoid bias. The primary outcome measure and unit of analysis must also be appropriately defined.