This document outlines a research study on understanding the relationship between learning strategies and learner autonomy towards student's academic achievement in language learning. The study aims to examine the level of learner autonomy among students, differences between high- and low-achieving students, the correlation between learning strategies and autonomy, and how autonomy can improve achievement. A quantitative design will be used, including a questionnaire to collect data on autonomy, strategies and achievement. Data will be analyzed using frequency, mean, standard deviation and content analysis to address the research questions.






![RESEARCH DESIGN
Quantitative Research Designs
Correlational Research (investigator use correlation statistical technique to describe and measure the
degree of association {or relationship} between two or more variables or sets of scores) The Explanatory
Design
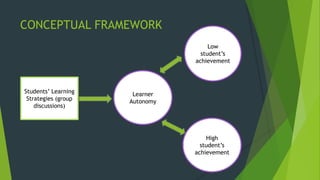
To see the correlational between learning strategies and learner autonomy.
To establish possible correlation between learner autonomy and student’s academic achievement
(high & low achiever)
Sample: Stratified Sampling (stratify the population on some specific characteristic [high & low
achiever] )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reseachproposalpresentation-150319225015-conversion-gate01/85/Reseach-proposal-presentation-8-320.jpg)

