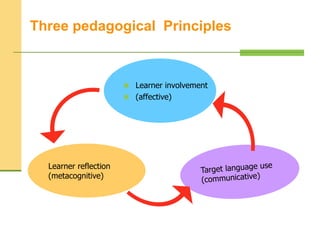
This seminar by Dr. Ahmed Khider explores the concept of autonomy learning in language acquisition, emphasizing its importance for both students and teachers. Attendees will learn about the characteristics of independent versus dependent learners, effective language learning strategies, and how to foster learner independence. The discussion also highlights the implications of autonomous learning for educators and the learning process.