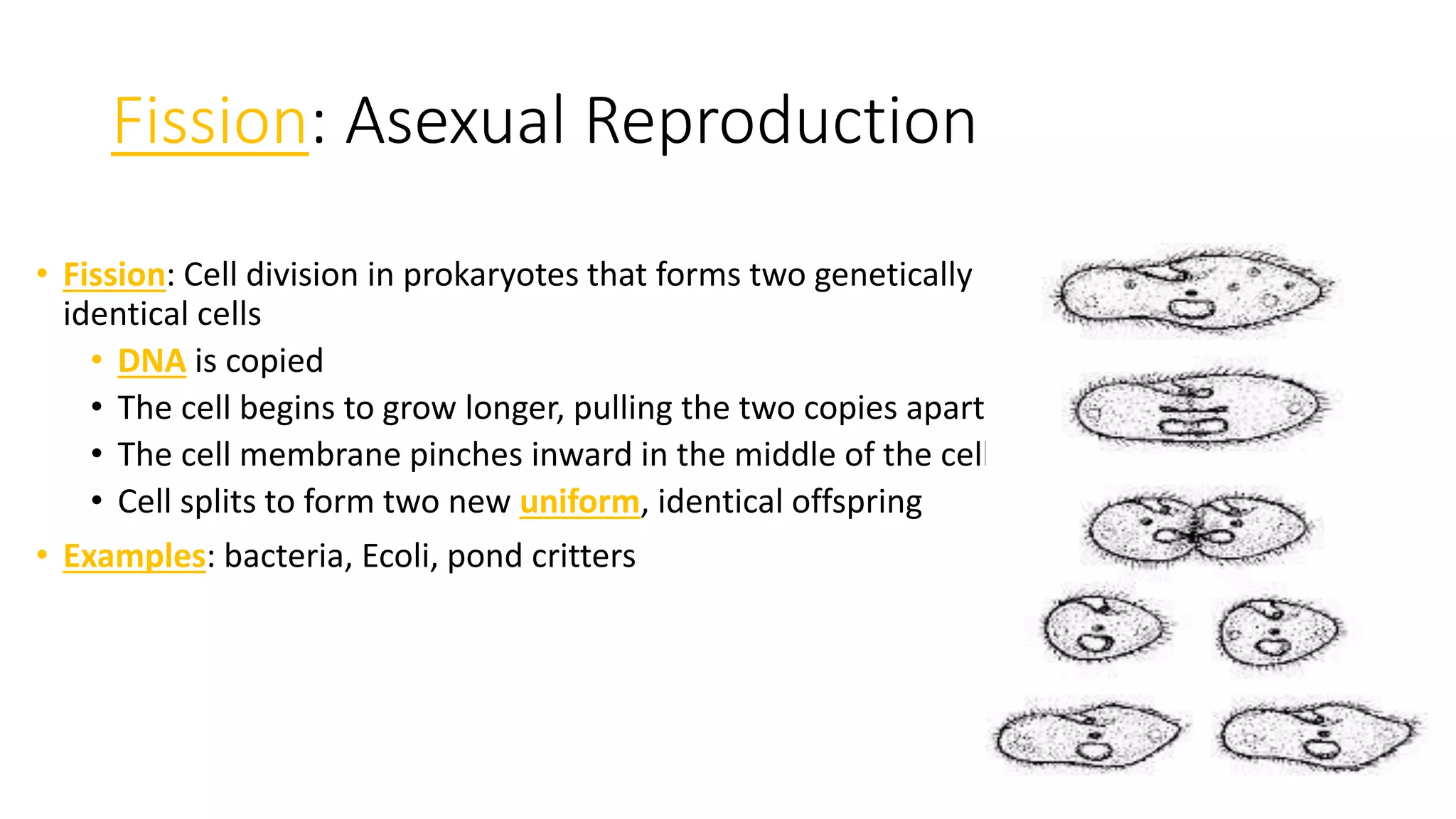
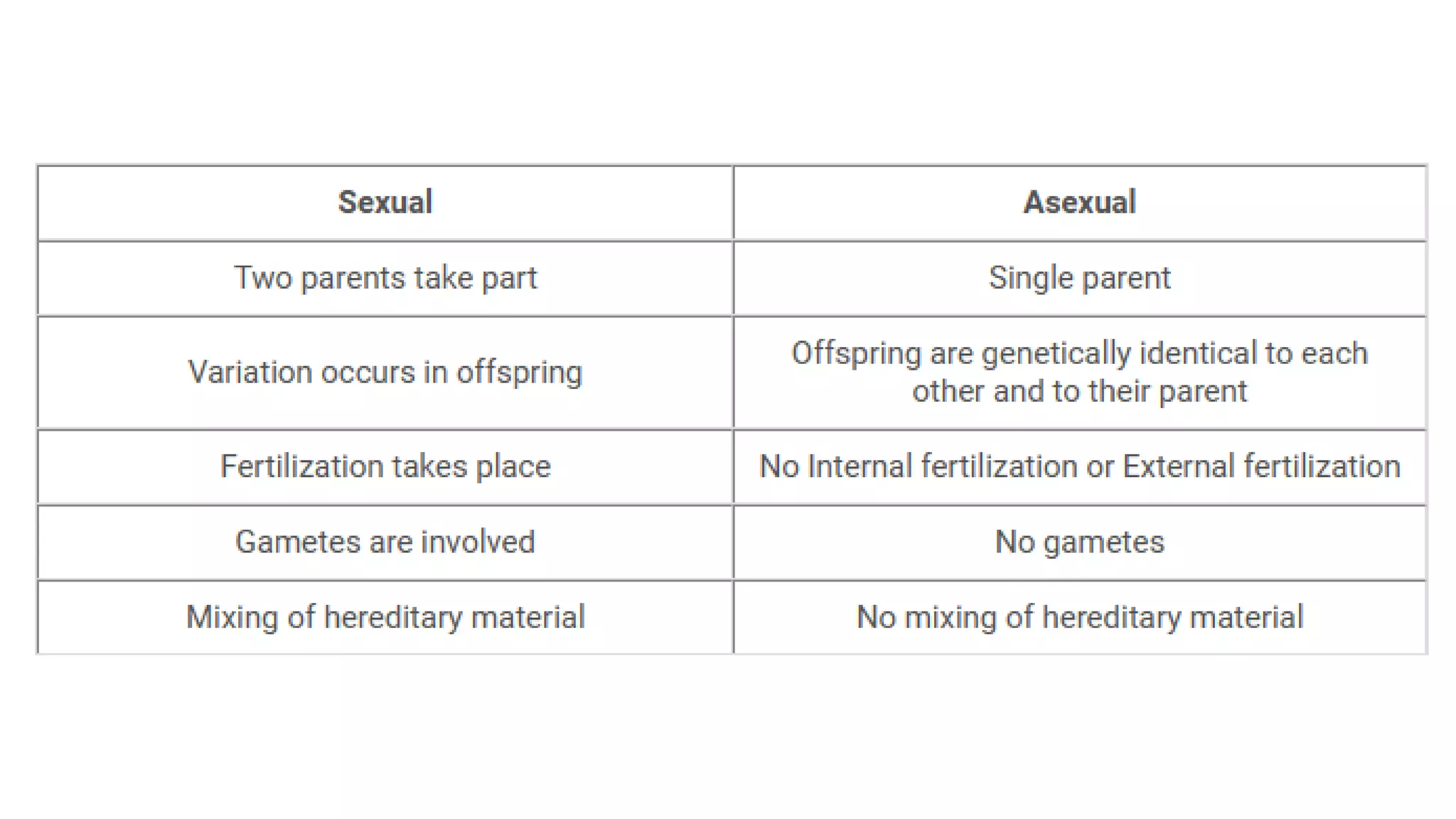
This document compares and contrasts sexual and asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction involves the combination of genetic material from two parent cells to form offspring that are genetically diverse. Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically uniform or identical to the parent. Some examples of asexual reproduction include binary fission, budding, vegetative propagation, and spore formation. Sexual reproduction provides genetic variation that allows populations to adapt, while asexual reproduction allows for rapid reproduction without the need for finding a mate but results in less genetic diversity.