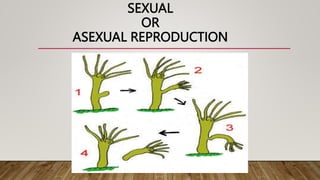
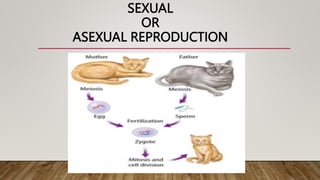
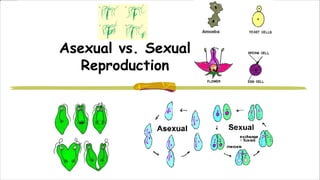
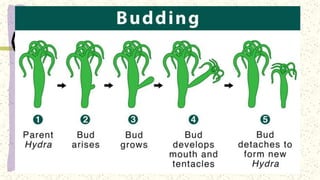
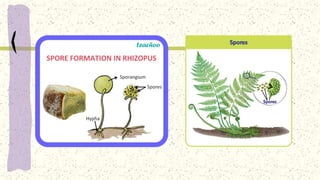
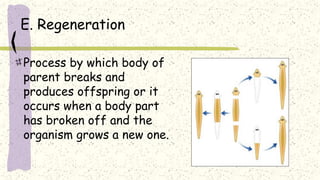
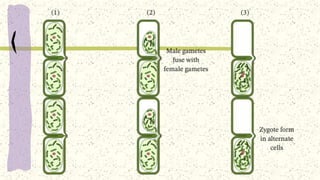
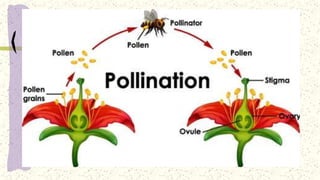
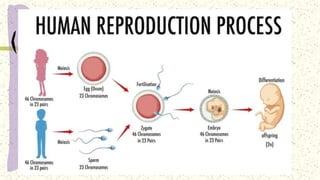
This document discusses and compares asexual and sexual reproduction. It defines asexual reproduction as reproduction involving only one parent that produces offspring identical to itself. Methods of asexual reproduction include vegetative reproduction, binary fission, budding, spore formation, and regeneration. Sexual reproduction involves the merging of genetic material from two parents to produce offspring with a combination of both parents' genes. Methods of sexual reproduction discussed include conjugation, pollination, and fertilization. The document aims to differentiate asexual and sexual reproduction in terms of the number of individuals involved and the genetic similarities between parents and offspring.