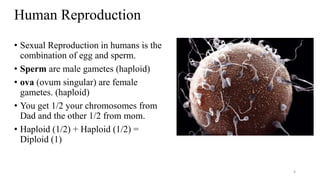
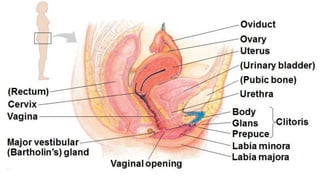
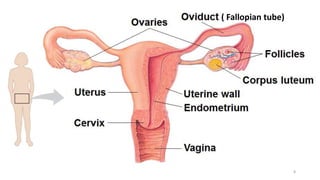
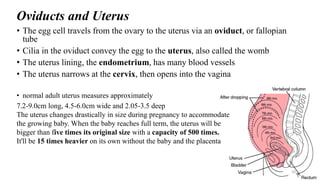
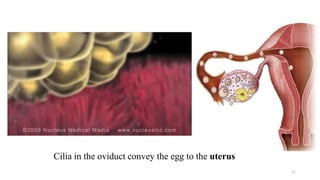
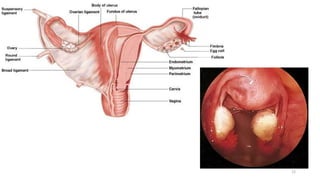
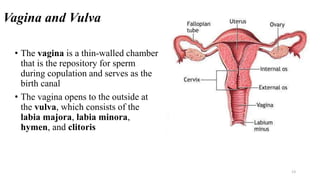
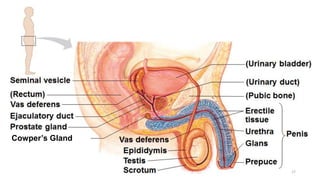
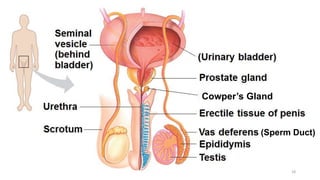
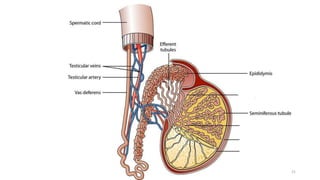
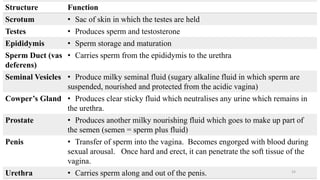
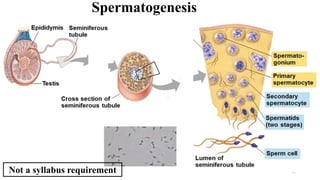
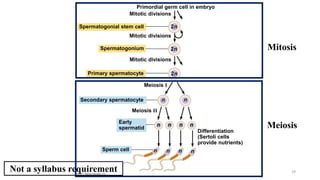
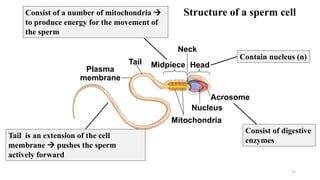
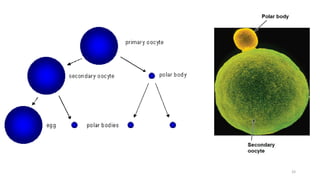
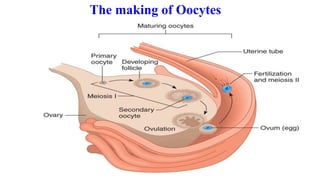
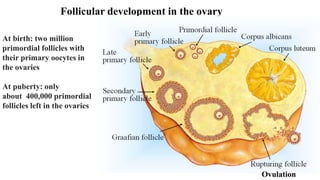
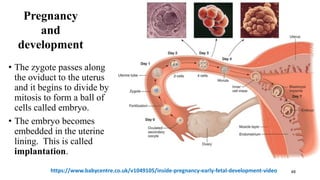
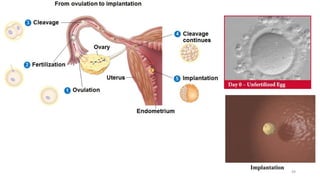
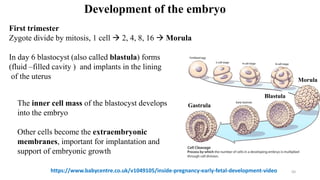
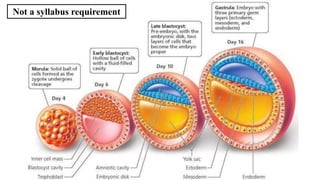
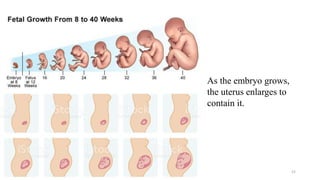
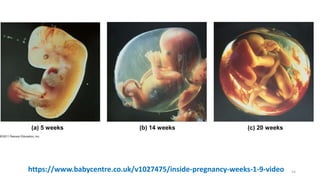
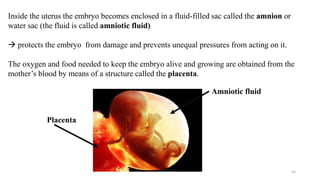
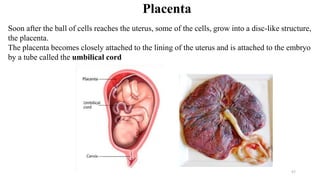
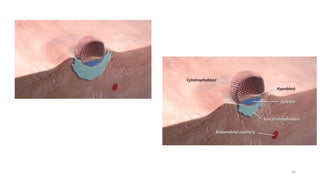
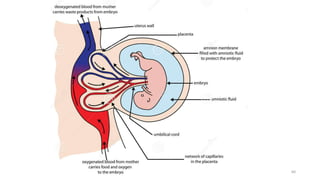
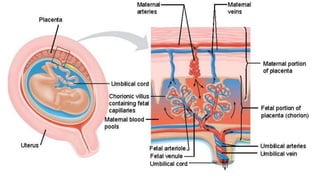
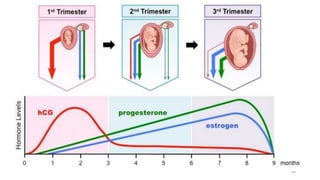
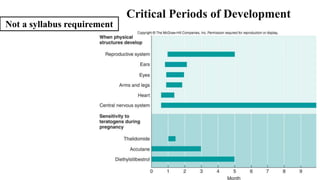
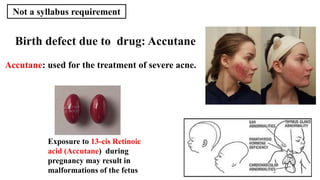
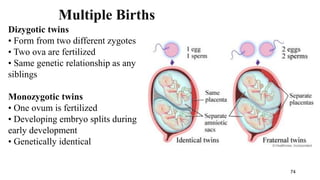
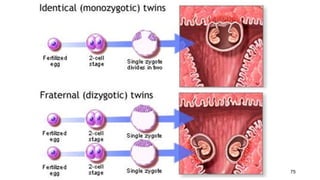
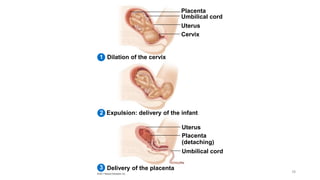
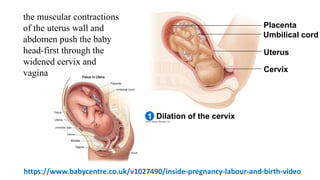
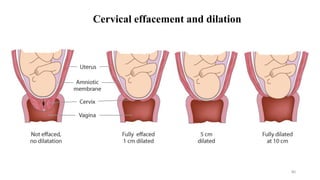
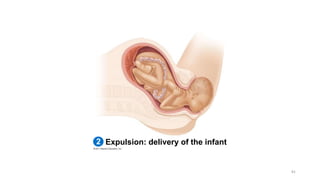
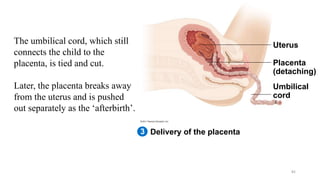
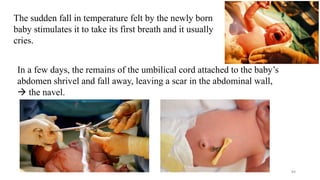
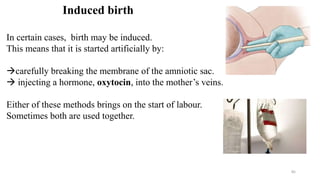
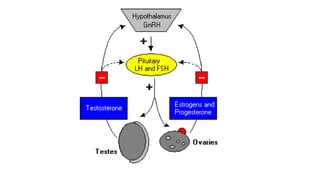
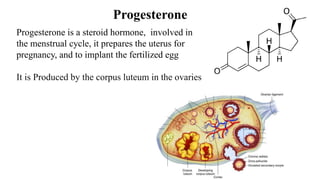
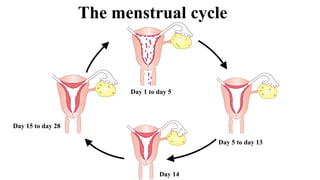
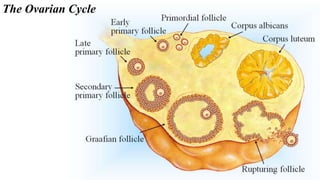
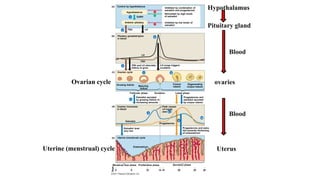
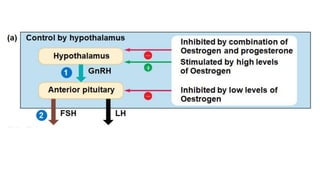
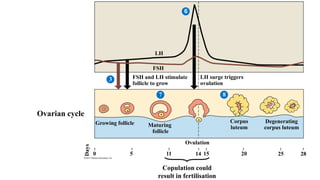
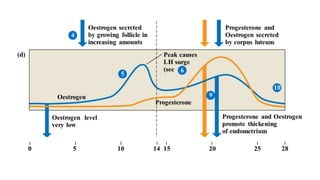
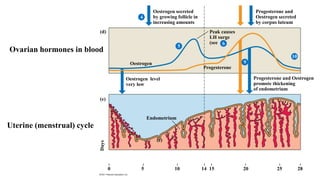
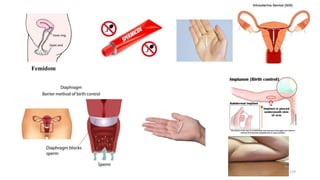
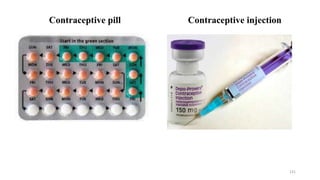
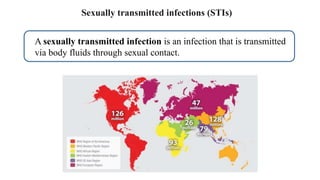
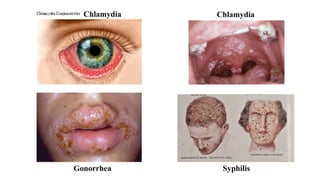
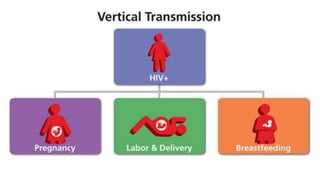
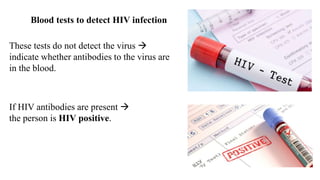
The placenta functions to exchange nutrients and waste between the mother and fetus. It attaches to the uterine wall and connects to the fetus via the umbilical cord. The placenta allows oxygen, glucose, amino acids and salts to pass from the mother's bloodstream to the fetus's bloodstream, while carbon dioxide and urea pass in the opposite direction, into the mother's bloodstream. This exchange occurs across the thin walls of the blood vessels without the bloodstreams directly mixing. The placenta regulates this exchange and protects the fetus from high blood pressure.