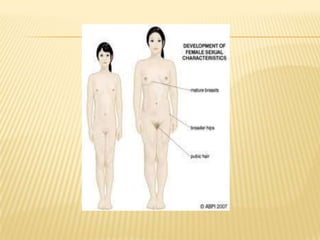
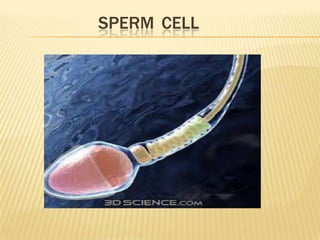
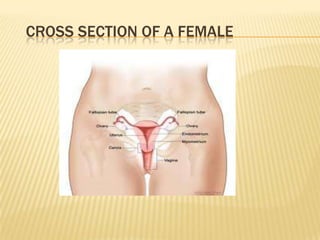
Human reproduction occurs through sexual reproduction which involves both male and female sex cells. At puberty, individuals develop primary and secondary sexual characteristics that differentiate males and females. Sperm and ova are the reproductive cells in males and females respectively. The male reproductive system includes testes, penis and other organs that produce and transport sperm. The female system includes ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes and other organs involved in producing and housing an embryo. Fertilization happens when a sperm joins an ovum, forming a zygote that implants in the uterus. Pregnancy lasts 9 months as the embryo develops protected structures until birth.