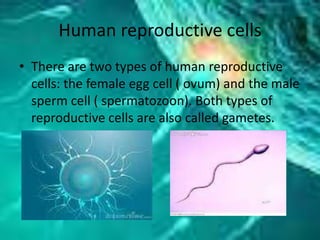
This document summarizes human reproduction. It describes the primary and secondary sex characteristics of males and females. It explains that reproduction requires both female egg cells and male sperm cells. It then details the female reproductive system including the external genitalia, internal organs, menstrual cycle, and pregnancy. It also outlines the male reproductive system including the penis, testicles, and role of semen. Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell joins with an egg cell to form a zygote, leading to pregnancy and eventual birth.