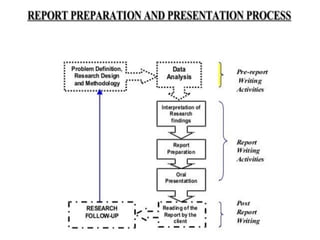
Research reports communicate the purpose, methodology, findings, and recommendations of a research project. They contain descriptions of the methodology used, results obtained, and recommendations made. The format of a research report includes an executive summary of major findings and conclusions, introduction, methodology, findings, and conclusions sections. Effective research reports are tailored to the technical expertise and interests of the intended audience, are well-organized and logically structured for easy understanding, and use visual aids to reinforce key information.

![• A research report is: a written document or oral
presentation based on a written document that
communicates the purpose, scope, objective(s),
hypotheses, methodology, findings, limitations
& finally, recommendations of a research
project to others.
• The researcher has to convince the client [&
others who may read the report] that the
research findings can be acted on for their own
benefit.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reportwritingandpresentationofdata-221006062312-fb2daf99/85/Report-Writing-and-Presentation-of-Data-pdf-2-320.jpg)