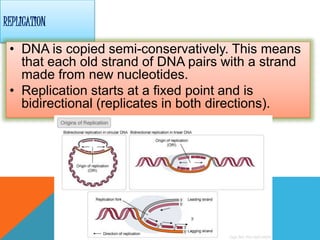
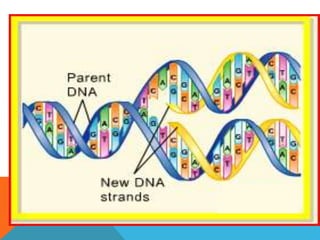
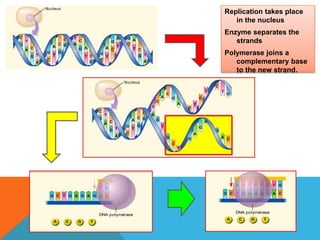
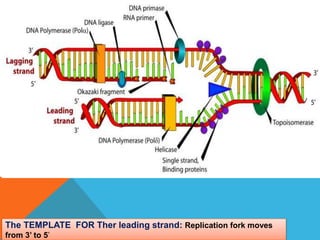
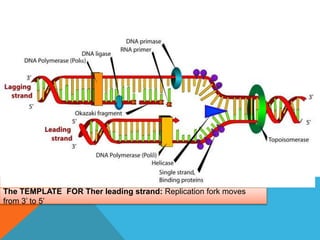
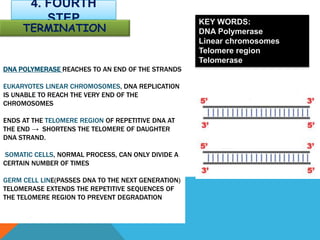
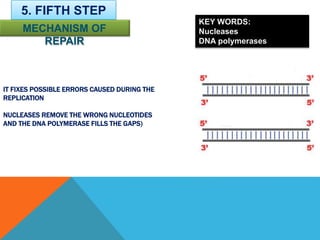
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA when it undergoes cell division. It occurs in the cell nucleus and uses a semi-conservative template mechanism based on complementary base pairing. The key steps are:
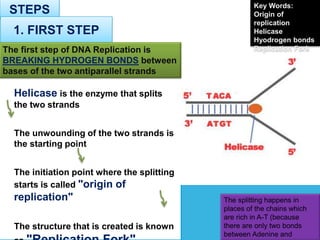
1) Helicase enzyme breaks the hydrogen bonds between the DNA strands, unwinding the double helix.
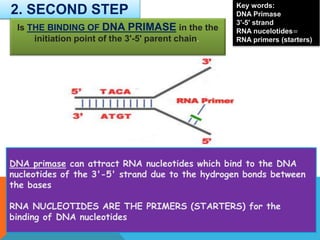
2) DNA primase binds to the unwound strands and adds RNA primers that will serve as starting points for DNA replication.
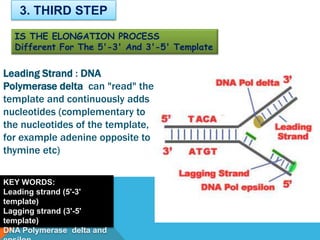
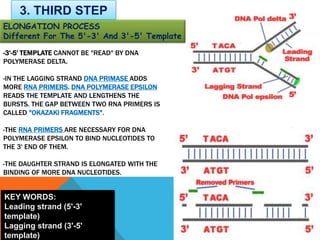
3) DNA polymerase then uses the parent strands as templates to build new complementary strands in a 5' to 3' direction by adding nucleotides, forming the leading strand continuously and the lagging strand in fragments called Okazaki fragments