This document provides a summary of key grammar points in Spanish, including:
- Present tense of regular verbs
- Stem-changing verbs
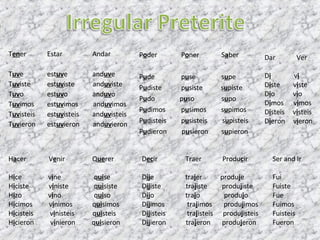
- Preterite tense of regular and irregular verbs
- Imperfect tense
- Present perfect and past perfect tenses
- Future tense
- Verbs like gustar
- Por vs para
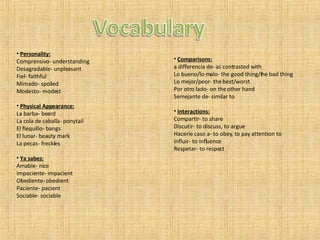
- Adjectives for personality, physical appearance, comparisons
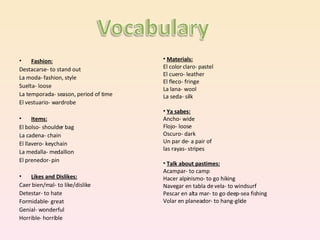
- Common verbs and vocabulary around fashion, pastimes, culture