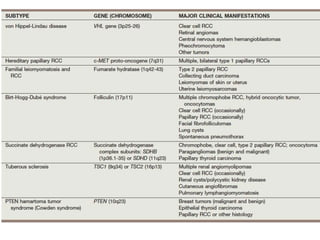
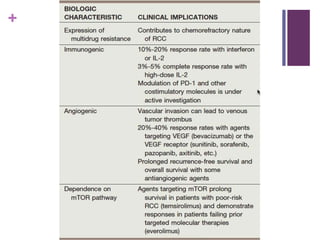
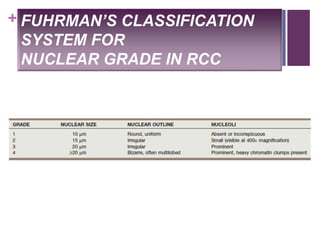
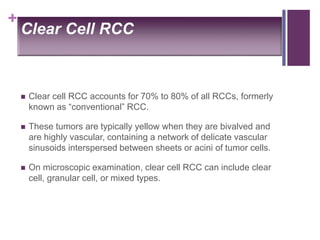
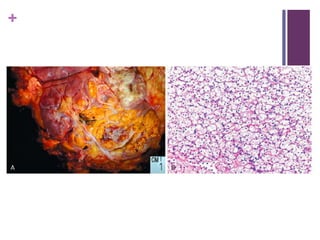
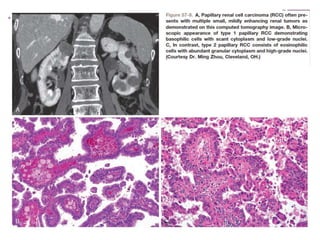
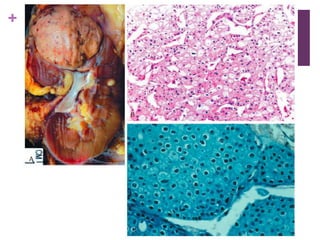
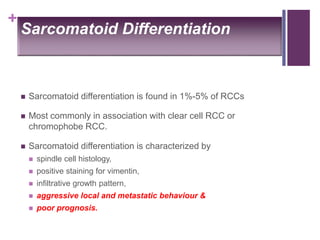
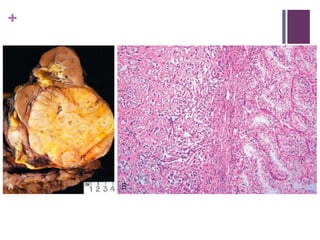
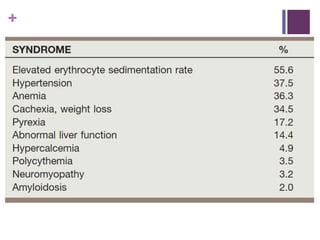
This document summarizes renal cell carcinoma (RCC), including its incidence, risk factors, pathology, subtypes, clinical presentation, and prognosis. RCC accounts for 2-3% of adult cancers and is the most lethal urologic cancer. Clear cell RCC is the most common subtype, accounting for 70-80% of cases. Other subtypes include papillary RCC, chromophobe RCC, collecting duct carcinoma, and unclassified RCC. Tumor size, grade, stage, and histologic subtype are important prognostic factors. Over 60% of RCCs are now detected incidentally with improved imaging techniques.