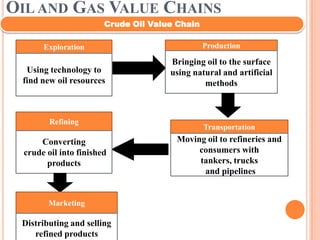
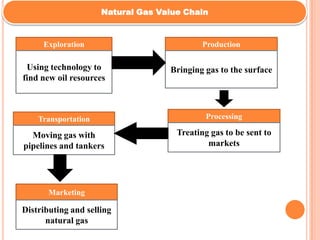
This document provides an overview of Reliance Industries Limited, an Indian petroleum and gas company. Key details include:
- It is a public company headquartered in Ahmedabad, India within the petroleum and gas industry.
- Founded in 2008, it is led by Mukesh Ambani and generates annual revenue of approximately 3,678 crore (US$665.72 million) primarily from petroleum products.
- It is a subsidiary of the Indian conglomerate Reliance Industries.